Page 130 - DECO101_MICRO_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 130
Unit 9: Cost Concepts
4. ATC first declines, reaches a minimum and rises thereafter. When ATC attains its minimum, Notes
MC equals ATC.
5. MC first declines, reaches a minimum and rises thereafter – MC equals AVC and ATC
when these curves attain their minimum values. Furthermore, MC lies below both AVC
and ATC when they are declining; it lies above them when they are rising.
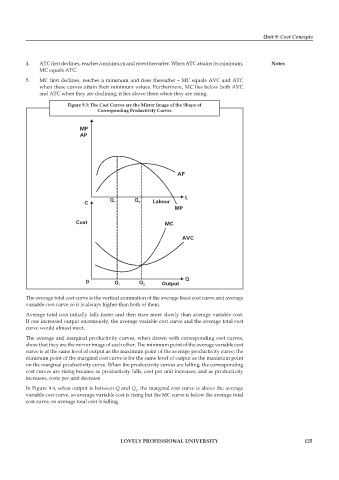
Figure 9.3: The Cost Curves are the Mirror Image of the Shape of
Corresponding Productivity Curves
MP
AP
AP
L
C Q 1 Q 2 Labour
MP
Cost MC
AVC
Q
0 Output
Q 1 Q 2
The average total cost curve is the vertical summation of the average fixed cost curve and average
variable cost curve so it is always higher than both of them.
Average total cost initially falls faster and then rises more slowly than average variable cost.
If one increased output enormously, the average variable cost curve and the average total cost
curve would almost meet.
The average and marginal productivity curves, when drawn with corresponding cost curves,
show that they are the mirror image of each other. The minimum point of the average variable cost
curve is at the same level of output as the maximum point of the average productivity curve; the
minimum point of the marginal cost curve is for the same level of output as the maximum point
on the marginal productivity curve. When the productivity curves are falling, the corresponding
cost curves are rising because as productivity falls, cost per unit increases; and as productivity
increases, costs per unit decrease.
In Figure 9.4, when output is between Q and Q , the marginal cost curve is above the average
1
variable cost curve, so average variable cost is rising but the MC curve is below the average total
cost curve, so average total cost is falling.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 125