Page 153 - DECO101_MICRO_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 153
Micro Economics
Notes
Did u know? All fi rms in the industry have the same minimum long run average cost. This,
however, does not meant have all firms have the same effi ciency.
10.3 Long Run Equilibrium of a Perfectly Competitive Firm
In the long run, all inputs and costs of production are variable and the firm can construct the
optimum or most appropriate scale of plant to produce the best level of output. The best level of
output is one at which price P=LMC equals the Long run Marginal Cost (LMC) of the fi rm. The
optimum scale of the plant is the one in which Short run Average Total Cost (SATC) curve is
tangent to the long run average cost of the firm at the best level of output. If existing fi rms earn
profits, however, more firms enter the market in the long run. This increases the market supply
of the product and results in a lower product price until all profits are squeezed out. On the other
hand, if firms in the market incur losses, some firms will leave the market in the long run. This
reduces the market supply of the product until all firms remaining in the market just break-even.
Thus, when a competitive market is in long run equilibrium, all firms produce at the lowest
point on their Long run Average Cost (LAC) curve and break-even. This is shown by point E in
Figure 10.8.
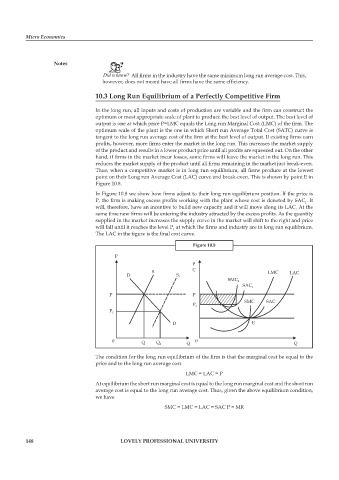
In Figure 10.8 we show how firms adjust to their long run equilibrium position. If the price is
P, the firm is making excess profits working with the plant whose cost is denoted by SAC . It
1
will, therefore, have an incentive to build new capacity and it will move along its LAC. At the
same time new firms will be entering the industry attracted by the excess profits. As the quantity
supplied in the market increases the supply curve in the market will shift to the right and price
will fall until it reaches the level P at which the fi rms and industry are in long run equilibrium.
1
The LAC in the figure is the final cost curve.
Figure 10.8
P
P
S C LMC LAC
D S 1
SMC 1
SAC 1
P P
SMC SAC
l
P 1
P 1
D E
0 Q Q 1 Q 0 Q
The condition for the long run equilibrium of the firm is that the marginal cost be equal to the
price and to the long run average cost.
LMC = LAC = P
At equilibrium the short run marginal cost is equal to the long run marginal cost and the short run
average cost is equal to the long run average cost. Thus, given the above equilibrium condition,
we have
SMC = LMC = LAC = SAC P = MR
148 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY