Page 209 - DECO101_MICRO_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 209
Micro Economics
Notes
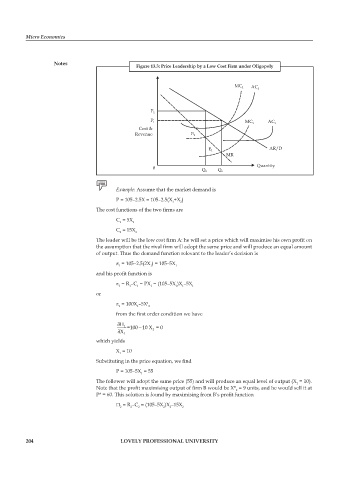
Figure 13.3: Price Leadership by a Low Cost Firm under Oligopoly
MC 2
AC 2
P 1
Cost & P 2 MC 1 AC 1
Revenue E 2
AR/D
E 1
MR
0 Q 2 Q 1 Quantity
Example: Assume that the market demand is
P = 105–2.5X = 105–2.5(X +X )
1 2
The cost functions of the two fi rms are
C = 5X
1 1
C = 15X
2 2
The leader will be the low cost firm A: he will set a price which will maximise his own profi t on
the assumption that the rival firm will adopt the same price and will produce an equal amount
of output. Thus the demand function relevant to the leader’s decision is
π = 105–2.5(2X ) = 105–5X 1
1
1
and his profit function is
π = R –C = PX = (105–5X )X –5X
1 1 1 1 1 1 1
or
π = 100X –5X
1
2
1
1
from the first order condition we have
∂Π
−
1 =100 10 X = 0
∂ X 1
1
which yields
X = 10
1
Substituting in the price equation, we fi nd
P = 105–5X = 55
1
The follower will adopt the same price (55) and will produce an equal level of output (X = 10).
2
Note that the profit maximising output of firm B would be X* = 9 units, and he would sell it at
2
P* = 60. This solution is found by maximising from B’s profi t function
Π = R –C = (105–5X )X –15X 2
2
2
2
2
2
204 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY