Page 216 - DECO101_MICRO_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 216
Unit 13: Oligopoly
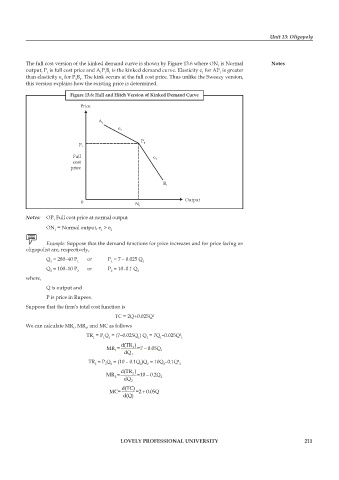
The full cost version of the kinked demand curve is shown by Figure 13.6 where ON is Normal Notes
1
output, P is full cost price and A P B is the kinked demand curve. Elasticity e for AP is greater
1
1
1
1
1
1
than elasticity e for P B . The kink occurs at the full cost price. Thus unlike the Sweezy version,
1
1
1
this version explains how the existing price is determined.
Figure 13.6: Hall and Hitch Version of Kinked Demand Curve
Price A 1 e 1
Full P 1 P 1
cost e 2
price
0 N 1 B 1 Output
Notes: OP Full cost price at normal output
1
ON = Normal output, e > e
1 1 2
Example: Suppose that the demand functions for price increases and for price facing an
oligopolist are, respectively,
Q = 280–40 P or P = 7 – 0.025 Q
1 1 1 1
Q = 100–10 P or P = 10–0.1 Q
2 2 2 2
where,
Q is output and
P is price in Rupees.
Suppose that the firm’s total cost function is
TC = 2Q+0.025Q 2
We can calculate MR , MR , and MC as follows
1 2
TR = P Q = (7–0.025Q ) Q = 7Q –0.025Q
2
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
d(TR )
MR = 1 =7 0.05Q 1
−
1
dQ 1
TR = P Q = (10 – 0.1Q )Q = 10Q –0.1Q
2
2 2 2 2 2 2 2
d(TR )
MR = 2 =10 0.2Q 2
-
2
dQ 2
d(TC)
MC= =2 0.05Q
+
d(Q)
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 211