Page 65 - DECO101_MICRO_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 65
Micro Economics
Notes
Example: When a thirsty person takes five bottles of cold drink continuously, the
consumption of first bottle gives him a high utility. The consumption of the second bottle gives
him lesser utility than first but his total utility increases. Third bottle gives him still less utility
but increases total utility. The utility from fourth bottle may be zero as he is no more thirsty. But
the fifth bottle may cause uneasiness and thus give negative utility, i.e., the total utility may now
actually go down.
Let’s understand this law with the help of an example given in Table below
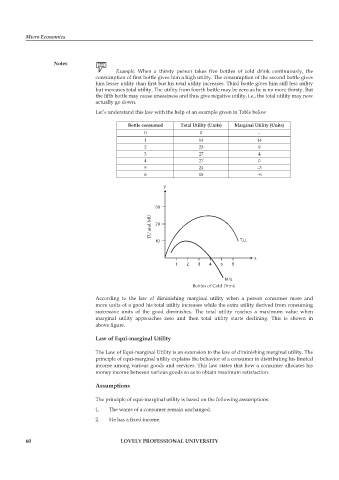
Bottle consumed Total Utility (Units) Marginal Utility (Units)
0 0 –
1 14 14
2 23 9
3 27 4
4 27 0
5 24 –3
6 18 –6
y
TU and MU
T.U.
x
M.U.
Bottles of Cold Drink
According to the law of diminishing marginal utility when a person consumes more and
more units of a good his total utility increases while the extra utility derived from consuming
successive units of the good diminishes. The total utility reaches a maximum value when
marginal utility approaches zero and then total utility starts declining. This is shown in
above fi gure.
Law of Equi-marginal Utility
The Law of Equi-marginal Utility is an extension to the law of diminishing marginal utility. The
principle of equi-marginal utility explains the behavior of a consumer in distributing his limited
income among various goods and services. This law states that how a consumer allocates his
money income between various goods so as to obtain maximum satisfaction.
Assumptions
The principle of equi-marginal utility is based on the following assumptions:
1. The wants of a consumer remain unchanged.
2. He has a fi xed income.
60 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY