Page 73 - DECO101_MICRO_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 73
Micro Economics
Notes comes to making a choice between them. Such a situation arises because he/she consumes a large
number of goods and services and often finds that one commodity can be substituted for another.
This gives him/her an opportunity to substitute one commodity for another, if need arises and
to make various combinations of two substitutable goods which give him/her the same level of
satisfaction. If a consumer faced with such combinations, he/she would be indifferent between
the combinations.
Example: If a consumer is asked whether he prefers combination 1 of two goods X and
Y (assuming that the market price of X and Y are fixed) or combination 2, he may give one of the
following answers:
1. he prefers combination 1 to 2
2. he prefers combination 2 to 1
3. he is indifferent about combinations 1 and 2.
The third answer implies that the consumer prefers 1 as much as 2. There may be some more
combinations of goods X and Y which are equally preferable to him. Suppose, there are fi ve
different combinations of X and Y, that gives him the same level of satisfaction.
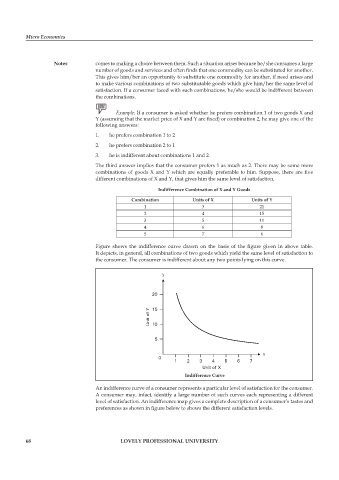
Indifference Combination of X and Y Goods
Combination Units of X Units of Y
1 3 21
2 4 15
3 5 11
4 6 8
5 7 6
Figure shows the indifference curve drawn on the basis of the figure given in above table.
It depicts, in general, all combinations of two goods which yield the same level of satisfaction to
the consumer. The consumer is indifferent about any two points lying on this curve.
y
x
Indifference Curve
An indifference curve of a consumer represents a particular level of satisfaction for the consumer.
A consumer may, infact, identify a large number of such curves each representing a different
level of satisfaction. An indifference map gives a complete description of a consumer’s tastes and
preferences as shown in figure below to shows the different satisfaction levels.
68 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY