Page 36 - DCOM203_DMGT204_QUANTITATIVE_TECHNIQUES_I
P. 36
Unit 2: Classification of Data
Solution: The determination of class boundaries depends upon the nature of approximation. Notes
Since the quoted age is the age completed on last birthday, therefore, a number greater than 29
but less than 30 is approximated as 29. Therefore, the boundaries of this class will be 20 - 30.
Similarly, the boundaries of other classes will be 30 - 40, 40 - 50 and 50 - 60, respectively.
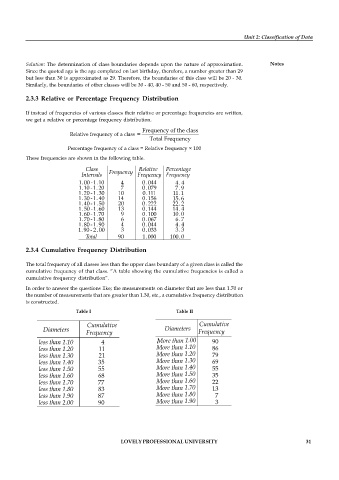
2.3.3 Relative or Percentage Frequency Distribution
If instead of frequencies of various classes their relative or percentage frequencies are written,
we get a relative or percentage frequency distribution.
Frequency of the class
Relative frequency of a class =
Total Frequency
Percentage frequency of a class = Relative frequency × 100
These frequencies are shown in the following table.
2.3.4 Cumulative Frequency Distribution
The total frequency of all classes less than the upper class boundary of a given class is called the
cumulative frequency of that class. “A table showing the cumulative frequencies is called a
cumulative frequency distribution”.
In order to answer the questions like; the measurements on diameter that are less than 1.70 or
the number of measurements that are greater than 1.30, etc., a cumulative frequency distribution
is constructed.
Table I Table II
4 90
11 86
21 79
35 69
55 55
68 35
77 22
83 13
87 7
90 3
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 31