Page 142 - DCOM204_AUDITING_THEORY
P. 142
Auditing Theory
Notes
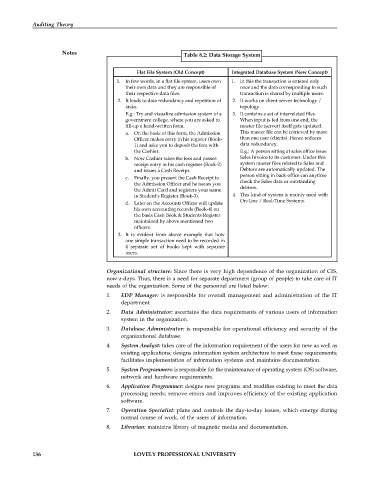
Table 8.2: Data Storage System
Flat File System (Old Concept) Integrated Database System (New Concept)
1. In few words, in a flat file system, users own 1. In this the transaction is entered only
their own data and they are responsible of once and the data corresponding to such
their respective data files. transaction is shared by multiple users.
2. It leads to data redundancy and repetition of 2. It works on client-server technology /
tasks. topology.
E.g.: Try and visualize admission system of a 3. It contains a set of interrelated files.
government college, where you are asked to When input is fed from one end, the
fill-up a hand-written form. master file (server) itself gets updated.
a. On the basis of this form, the Admission This master file can be retrieved by more
Officer makes entry in his register (Book- than one user (clients). Hence reduces
1) and asks you to deposit the fees with data redundancy.
the Cashier. E.g.: A person sitting at sales office issue
b. Now Cashier takes the fees and passes Sales Invoice to its customer. Under this
receipt entry in his cash register (Book-2) system master files related to Sales and
and issues a Cash Receipt. Debtors are automatically updated. The
person sitting in back-office can anytime
c. Finally, you present the Cash Receipt to
the Admission Officer and he issues you check the Sales data or outstanding
the Admit Card and registers your name debtors.
in Student’s Register (Book-3). 4. This kind of system is mainly used with
On-Line / Real-Time Systems.
d. Later on the Accounts Officer will update
his own accounting records (Book-4) on
the basis Cash Book & Students Register
maintained by above mentioned two
officers.
3. It is evident from above example that how
one simple transaction need to be recorded in
4 separate set of books kept with separate
users.
Organizational structure: Since there is very high dependence of the organization of CIS,
now-a-days. Thus, there is a need for separate department (group of people) to take care of IT
needs of the organization. Some of the personnel are listed below:
1. EDP Manager: is responsible for overall management and administration of the IT
department.
2. Data Administrator: ascertains the data requirements of various users of information
system in the organization.
3. Database Administrator: is responsible for operational efficiency and security of the
organizational database.
4. System Analyst: takes care of the information requirement of the users for new as well as
existing applications; designs information system architecture to meet these requirements;
facilitates implementation of information systems and maintains documentation.
5. System Programmers: is responsible for the maintenance of operating system (OS) software,
network and hardware requirements.
6. Application Programmer: designs new programs and modifies existing to meet the data
processing needs; remove errors and improves efficiency of the existing application
software.
7. Operation Specialist: plans and controls the day-to-day issues, which emerge during
normal course of work, of the users of information.
8. Librarian: maintains library of magnetic media and documentation.
136 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY