Page 4 - DCOM204_AUDITING_THEORY
P. 4
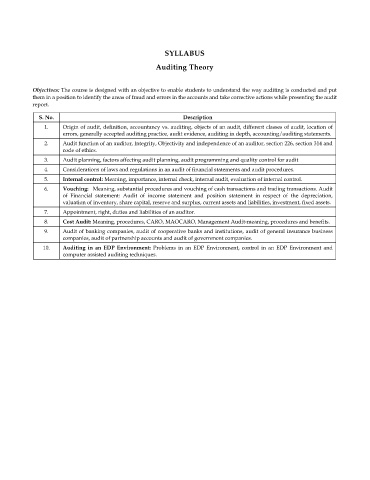
SYLLABUS
Auditing Theory
Objectives: The course is designed with an objective to enable students to understand the way auditing is conducted and put
them in a position to identify the areas of fraud and errors in the accounts and take corrective actions while presenting the audit
report.
S. No. Description
1. Origin of audit, definition, accountancy vs. auditing, objects of an audit, different classes of audit, location of
errors, generally accepted auditing practice, audit evidence, auditing in depth, accounting/auditing statements.
2. Audit function of an auditor, Integrity, Objectivity and independence of an auditor, section 226, section 314 and
code of ethics.
3. Audit planning, factors affecting audit planning, audit programming and quality control for audit
4. Considerations of laws and regulations in an audit of financial statements and audit procedures.
5. Internal control: Meaning, importance, internal check, internal audit, evaluation of internal control.
6. Vouching: Meaning, substantial procedures and vouching of cash transactions and trading transactions. Audit
of Financial statement: Audit of income statement and position statement in respect of the depreciation,
valuation of inventory, share capital, reserve and surplus, current assets and liabilities, investment, fixed assets.
7. Appointment, right, duties and liabilities of an auditor.
8. Cost Audit: Meaning, procedures, CARO, MAOCARO, Management Audit-meaning, procedures and benefits.
9. Audit of banking companies, audit of cooperative banks and institutions, audit of general insurance business
companies, audit of partnership accounts and audit of government companies.
10. Auditing in an EDP Environment: Problems in an EDP Environment, control in an EDP Environment and
computer assisted auditing techniques.