Page 144 - DECO201_MACRO_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 144
Unit 8: Money
In India, the parallel broad money measure is labelled M . It equals: Notes
3
M (India) = M
3 1
+ Time deposits with banks.
Self Assessment
Fill in the blanks:
6. M measure of money is also called the transaction or .............................. money.
1
7. In India, M1 includes currency held outside banks and ..............................
8. Time deposits are primarily ..............................accounts.
9. Assets that are close substitutes of money are called ..............................
10. M = M + ___________
3 1
8.3 Demand for Money
Demand means holding. People hold money to carry out transactions, like buying, selling,
borrowing, lending, etc. The main factors that influence how much money people will hold
(demand) are: rate of interest, GDP and price level. The money is held as cash and as deposits in
chequable accounts.
8.3.1 Factors affecting Demand for Money
The factors that affect the demand for money are:
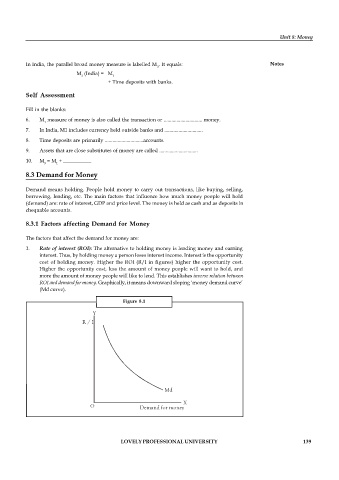
1. Rate of interest (ROI): The alternative to holding money is lending money and earning
interest. Thus, by holding money a person loses interest income. Interest is the opportunity
cost of holding money. Higher the ROI (R/I in figures) higher the opportunity cost.
Higher the opportunity cost, less the amount of money people will want to hold, and
more the amount of money people will like to lend. This establishes inverse relation between
ROI and demand for money. Graphically, it means downward sloping ‘money demand curve’
(Md curve).
Figure 8.1
Y
R / I
Md
X
O Demand for money
Figure. 12.1
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 139