Page 80 - DECO201_MACRO_ECONOMICS_ENGLISH
P. 80
Unit 4: Theories of Income, Output and Employment: Keynesian Theory
Decrease in AE, aggregate supply remaining unchanged, leads to rise in inventories. Notes
Rise in inventories leads to fall in equilibrium output/income (Y).
This establishes inverse relation between P and equilibrium Y.
Derivation of the AD Curve
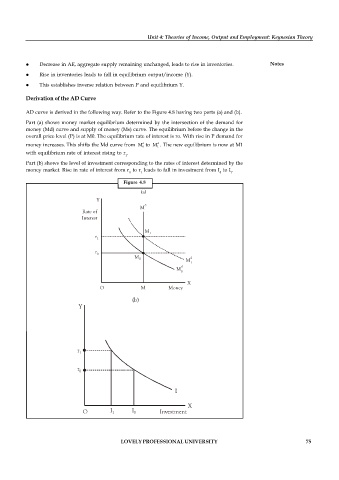
AD curve is derived in the following way. Refer to the Figure 4.8 having two parts (a) and (b).
Part (a) shows money market equilibrium determined by the intersection of the demand for
money (Md) curve and supply of money (Ms) curve. The equilibrium before the change in the
overall price level (P) is at M0. The equilibrium rate of interest is ro. With rise in P demand for
d
d
money increases. This shifts the Md curve from M to M . The new equilibrium is now at M1
0
1
with equilibrium rate of interest rising to r .
1
Part (b) shows the level of investment corresponding to the rates of interest determined by the
money market. Rise in rate of interest from r to r leads to fall in investment from I to I .
0 1 0 1
Figure 4.8
(a)
Y
S
M
Rate of
Interest
M 1
r 1
r 0
M d
0 M
1
M d
0
X
O M Money
(b)
Y
r 1
r 0
I
X
O I 1 I 0 Investment
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 75