Page 264 - DCOM206_COST_ACCOUNTING_II
P. 264
Unit 14: Emerging Concepts in Cost Management
Three useful strategic frameworks for value chain analysis are: Notes
Industry structure analysis
Core competencies
Segmentation analysis
14.4.1 Industry Structure Analysis
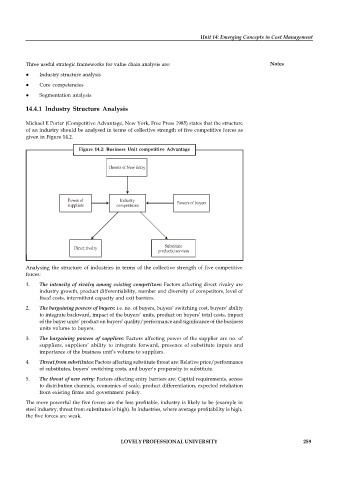
Michael E Porter (Competitive Advantage, New York, Free Press 1985) states that the structure
of an industry should be analysed in terms of collective strength of five competitive forces as
given in Figure 14.2.
Figure 14.2: Business Unit competitive Advantage
Analysing the structure of industries in terms of the collective strength of five competitive
forces:
1. The intensity of rivalry among existing competitors: Factors affecting direct rivalry are
industry growth, product differentiability, number and diversity of competitors, level of
fixed costs, intermittent capacity and exit barriers.
2. The bargaining powers of buyers: i.e. no. of buyers, buyers’ switching cost, buyers’ ability
to integrate backward, impact of the buyers’ units, product on buyers’ total costs, impact
of the buyer units’ product on buyers’ quality/performance and significance of the business
units volume to buyers.
3. The bargaining powers of suppliers: Factors affecting power of the supplier are no. of
suppliers, suppliers’ ability to integrate forward, presence of substitute inputs and
importance of the business unit’s volume to suppliers.
4. Threat from substitutes: Factors affecting substitute threat are: Relative price/performance
of substitutes, buyers’ switching costs, and buyer’s propensity to substitute.
5. The threat of new entry: Factors affecting entry barriers are: Capital requirements, access
to distribution channels, economies of scale, product differentiation, expected retaliation
from existing firms and government policy.
The more powerful the five forces are the less profitable, industry is likely to be (example in
steel industry, threat from substitutes is high). In industries, where average profitability is high,
the five forces are weak.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 259