Page 165 - DCOM208_BANKING_THEORY_AND_PRACTICE
P. 165
Banking Theory and Practice
Notes the court will discharge him. If accused is pronounced, then he needs to suspend his
sentence, for a period of 30 days with in which time, he can file an appeal before the
sessions court.
Task Visit your nearest bank and find out the common reasons for dishonour of cheque
that are known by the bank officials.
10.1.6 Crossing of Cheques
Crossing is a popular practice devised for protecting the drawer and payee of a cheque in case it
is lost, stolen or the signature is done by some other person for endorsing it. Both bearer and
order cheques can be crossed. Crossing prevents fraud and faulty payments. Crossing of a
cheque means “Drawing Two Parallel Lines” across the front of the cheque. Thus, crossing is
essential in order that safety is maintained.
Notes Crossed cheques must be presented through the bank only because they are not
encashed at the counter.
Different Types of Crossing
Cheques can be crossed in following ways:
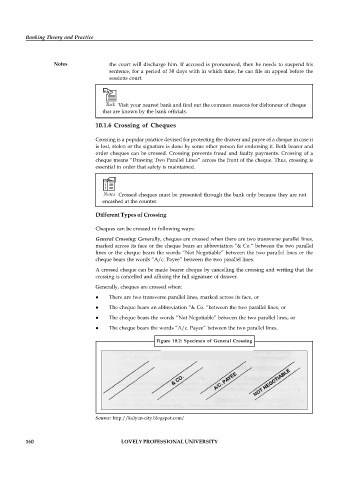
General Crossing: Generally, cheques are crossed when there are two transverse parallel lines,
marked across its face or the cheque bears an abbreviation “& Co.“ between the two parallel
lines or the cheque bears the words “Not Negotiable” between the two parallel lines or the
cheque bears the words “A/c. Payee” between the two parallel lines.
A crossed cheque can be made bearer cheque by cancelling the crossing and writing that the
crossing is cancelled and affixing the full signature of drawer.
Generally, cheques are crossed when:
There are two transverse parallel lines, marked across its face, or
The cheque bears an abbreviation “& Co. “between the two parallel lines, or
The cheque bears the words “Not Negotiable” between the two parallel lines, or
The cheque bears the words “A/c. Payee” between the two parallel lines.
Figure 10.2: Specimen of General Crossing
Source: http://kalyan-city.blogspot.com/
160 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY