Page 64 - DCOM208_BANKING_THEORY_AND_PRACTICE
P. 64
Unit 4: Credit Creation
keeping a cash reserve of ` 90, Bank B is free to lend the balance of ` 810 to anyone. Suppose bank Notes
B lends ` 810 to Z, who uses the amount to pay off his creditors. The balance sheet of bank B will
be as follows:
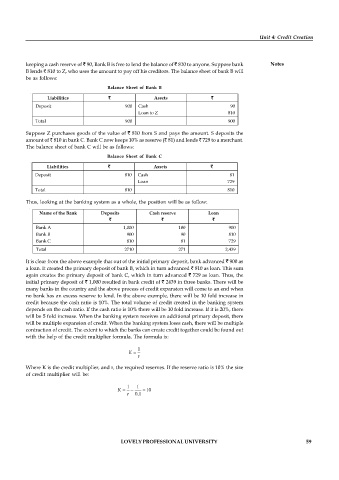
Balance Sheet of Bank B
Liabilities ` Assets `
Deposit 900 Cash 90
Loan to Z 810
Total 900 900
Suppose Z purchases goods of the value of ` 810 from S and pays the amount. S deposits the
amount of ` 810 in bank C. Bank C now keeps 10% as reserve (` 81) and lends ` 729 to a merchant.
The balance sheet of bank C will be as follows:
Balance Sheet of Bank C
Liabilities ` Assets `
Deposit 810 Cash 81
Loan 729
Total 810 810
Thus, looking at the banking system as a whole, the position will be as follow:
Name of the Bank Deposits Cash reserve Loan
` ` `
Bank A 1,000 100 900
Bank B 900 90 810
Bank C 810 81 729
Total 2710 271 2,439
It is clear from the above example that out of the initial primary deposit, bank advanced ` 900 as
a loan. It created the primary deposit of bank B, which in turn advanced ` 810 as loan. This sum
again creates the primary deposit of bank C, which in turn advanced ` 729 as loan. Thus, the
initial primary deposit of ` 1,000 resulted in bank credit of ` 2439 in three banks. There will be
many banks in the country and the above process of credit expansion will come to an end when
no bank has an excess reserve to lend. In the above example, there will be 10 fold increase in
credit because the cash ratio is 10%. The total volume of credit created in the banking system
depends on the cash ratio. If the cash ratio is 10% there will be 10 fold increase. If it is 20%, there
will be 5 fold increase. When the banking system receives an additional primary deposit, there
will be multiple expansion of credit. When the banking system loses cash, there will be multiple
contraction of credit. The extent to which the banks can create credit together could be found out
with the help of the credit multiplier formula. The formula is:
1
K =
r
Where K is the credit multiplier, and r, the required reserves. If the reserve ratio is 10% the size
of credit multiplier will be:
1 1
K = − = 10
r 01
.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 59