Page 174 - DCOM302_MANAGEMENT_ACCOUNTING
P. 174
Unit 9: Variance Analysis
Notes
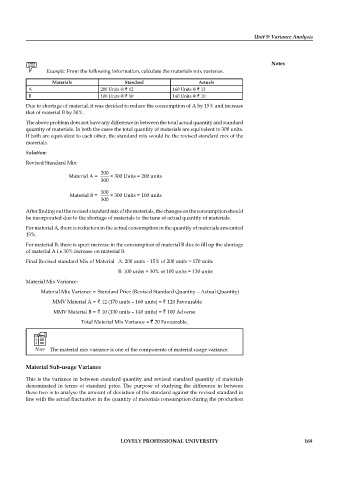
Example: From the following information, calculate the materials mix variance.
Materials Standard Actuals
A 200 Units @ ` 12 160 Units @ ` 13
B 100 Units @ ` 10 140 Units @ ` 10
Due to shortage of material, it was decided to reduce the consumption of A by 15% and increase
that of material B by 30%.
The above problem does not have any difference in between the total actual quantity and standard
quantity of materials. In both the cases the total quantity of materials are equivalent to 300 units.
If both are equivalent to each other, the standard mix would be the revised standard mix of the
materials.
Solution:
Revised Standard Mix:
200
Material A = × 300 Units = 200 units
300
100
Material B = × 300 Units = 100 units
300
After finding out the revised standard mix of the materials, the changes on the consumption should
be incorporated due to the shortage of materials to the tune of actual quantity of materials.
For material A, there is reduction in the actual consumption in the quantity of materials amounted
15%.
For material B, there is spurt increase in the consumption of material B due to fill up the shortage
of material A i.e 30% increase on material B.
Final Revised standard Mix of Material A: 200 units – 15% of 200 units = 170 units
B: 100 units + 30% of 100 units = 130 units
Material Mix Variance:
Material Mix Variance = Standard Price (Revised Standard Quantity – Actual Quantity)
MMV Material A = ` 12 (170 units – 160 units) = ` 120 Favourable
MMV Material B = ` 10 (130 units – 140 units) = ` 100 Adverse
Total Material Mix Variance = ` 20 Favourable.
Note The material mix variance is one of the components of material usage variance.
Material Sub-usage Variance
This is the variance in between standard quantity and revised standard quantity of materials
denominated in terms of standard price. The purpose of studying the difference in between
these two is to analyse the amount of deviation of the standard against the revised standard in
line with the actual fluctuation in the quantity of materials consumption during the production
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 169