Page 182 - DCOM302_MANAGEMENT_ACCOUNTING
P. 182
Unit 9: Variance Analysis
What is normal idle time? Notes
This idle time is known as authorised idle time, which can be understood in other words as
unavoidable idle time. Normally, the worker is paid for that time during which he does not
produce anything.
Time taken by the employees to change the dress.
Time take by the employees to ease themselves during the hours of production i.e going to the
toilet for easing and for refreshment going to the canteen.
The employees are paid during the above-enlisted occasions at when they do not produce
anything
In between two different shifts, the production of finished goods do not normally take place due
to change over the control from one employee to another.
What is meant by abnormal idle time?
This is known as avoidable idle time; during which the workers are paid for nil production. This
type of idle time could be slashed down or downsized through an effective planning. This idle
time is the resultant of too many ineffective schedules, e.g. inadequate supply of raw materials,
power shortage/failure, breakdown of machinery and so on. The aforementioned could be
easily sorted out through proper planning and scheduling; which will automatically reduce the
unproductive time of labour force. Whatever the payment of wages to the working force during
the idle time are to be considered as adverse. It means that the firm makes the payment of wages
to the labourers/working force without any production/productivity.
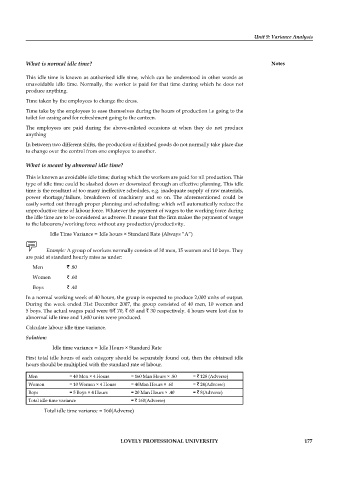
Idle Time Variance = Idle hours × Standard Rate (Always “A”)
Example: A group of workers normally consists of 30 men, 15 women and 10 boys. They
are paid at standard hourly rates as under:
Men ` .80
Women ` .60
Boys ` .40
In a normal working week of 40 hours, the group is expected to produce 2,000 units of output.
During the week ended 31st December 2007, the group consisted of 40 men, 10 women and
5 boys. The actual wages paid were @` 70, ` 65 and ` 30 respectively. 4 hours were lost due to
abnormal idle time and 1,600 units were produced.
Calculate labour idle time variance.
Solution:
Idle time variance = Idle Hours × Standard Rate
First total idle hours of each category should be separately found out, then the obtained idle
hours should be multiplied with the standard rate of labour.
Men = 40 Men × 4 Hours = 160 Man Hours × .80 = ` 128 (Adverse)
Women = 10 Women × 4 Hours = 40Man Hours × .60 = ` 24(Adverse)
Boys = 5 Boys × 4 Hours = 20 Man Hours × .40 = ` 8(Adverse)
Total idle time variance = ` 160(Adverse)
Total idle time variance = 160(Adverse)
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 177