Page 9 - DCOM302_MANAGEMENT_ACCOUNTING
P. 9
Management Accounting
Notes Though some number of differences can be identified between cost accounting and management
accounting, the line of difference is very thin. Because, cost accounting, at present, comprises of
some of the advanced techniques and systems of costing such as budgetary control, marginal
costing, standard costing, etc. and therefore, it tends to conform to management accounting.
Consequently, not much difference can be found between the two. The main differences between
cost accounting and management accounting are given as under:
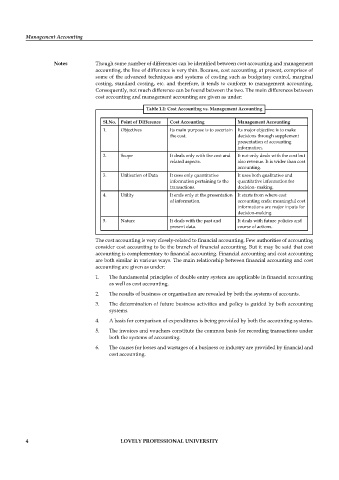
Table 1.1: Cost Accounting vs. Management Accounting
Sl.No. Point of Difference Cost Accounting Management Accounting
1. Objectives Its main purpose is to ascertain Its major objective is to make
the cost. decisions through supplement
presentation of accounting
information.
2. Scope It deals only with the cost and It not only deals with the cost but
related aspects. also revenue. It is wider than cost
accounting.
3. Utilisation of Data It uses only quantitative It uses both qualitative and
information pertaining to the quantitative information for
transactions. decision- making.
4. Utility It ends only at the presentation It starts from where cost
of information. accounting ends; meaningful cost
informations are major inputs for
decision-making.
5. Nature It deals with the past and It deals with future policies and
present data. course of actions.
The cost accounting is very closely-related to financial accounting. Few authorities of accounting
consider cost accounting to be the branch of financial accounting. But it may be said that cost
accounting is complementary to financial accounting. Financial accounting and cost accounting
are both similar in various ways. The main relationship between financial accounting and cost
accounting are given as under:
1. The fundamental principles of double entry system are applicable in fi nancial accounting
as well as cost accounting.
2. The results of business or organisation are revealed by both the systems of accounts.
3. The determination of future business activities and policy is guided by both accounting
systems.
4. A basis for comparison of expenditures is being provided by both the accounting systems.
5. The invoices and vouchers constitute the common basis for recording transactions under
both the systems of accounting.
6. The causes for losses and wastages of a business or industry are provided by fi nancial and
cost accounting.
4 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY