Page 134 - DCOM303_DMGT504_OPERATION_RESEARCH
P. 134
Unit 6: Transportation Problem – Optimality Tests
Linear Programming formulation, Notes
Minimize Z = 4X +7X +6X +3X +7X +4X +3X +5X +5X +6X +7X +8X
13 14 22 24 35 36 37 38 45 46 47 48
Subject to constraints,
X + X 14 800
13
X + X 600 origin constraints
23 23
–X –X + X + X + X + X = 0
13 23 35 36 37 38
–X –X + X + X + X + X = 0
14 24 45 46 47 48
!
Caution Don’t confuse between transportation and transshipment problem
A transportation problem can be converted into a transshipment problem by relaxing the
restrictions on the receiving and sending the units on the origins and destinations
respectively. A m-origin, n-destination, transportation problem, when expressed as
transshipment problem, shall become an enlarged problem: with m + n origins and an
equal number of destinations. With minor modifications, this problem can be solved
using the transportation method.
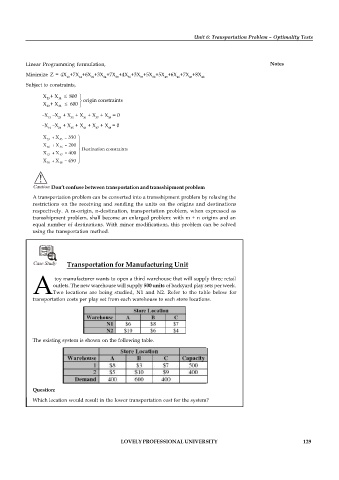
Case Study Transportation for Manufacturing Unit
toy manufacturer wants to open a third warehouse that will supply three retail
outlets. The new warehouse will supply 500 units of backyard play sets per week.
ATwo locations are being studied, N1 and N2. Refer to the table below for
transportation costs per play set from each warehouse to each store locations.
The existing system is shown on the following table.
Question:
Which location would result in the lower transportation cost for the system?
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 129