Page 291 - DCOM303_DMGT504_OPERATION_RESEARCH
P. 291
Operations Research
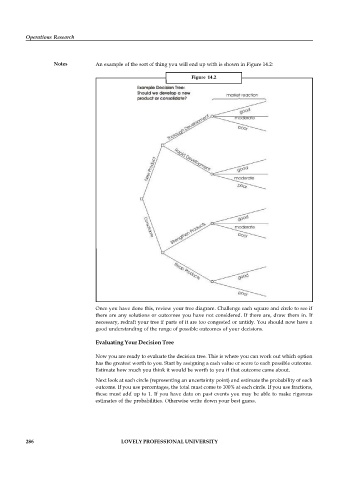
Notes An example of the sort of thing you will end up with is shown in Figure 14.2:
Figure 14.2
Once you have done this, review your tree diagram. Challenge each square and circle to see if
there are any solutions or outcomes you have not considered. If there are, draw them in. If
necessary, redraft your tree if parts of it are too congested or untidy. You should now have a
good understanding of the range of possible outcomes of your decisions.
Evaluating Your Decision Tree
Now you are ready to evaluate the decision tree. This is where you can work out which option
has the greatest worth to you. Start by assigning a cash value or score to each possible outcome.
Estimate how much you think it would be worth to you if that outcome came about.
Next look at each circle (representing an uncertainty point) and estimate the probability of each
outcome. If you use percentages, the total must come to 100% at each circle. If you use fractions,
these must add up to 1. If you have data on past events you may be able to make rigorous
estimates of the probabilities. Otherwise write down your best guess.
286 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY