Page 154 - DCOM304_INDIAN_FINANCIAL_SYSTEM
P. 154
Unit 8: Financial Institutions
Notes
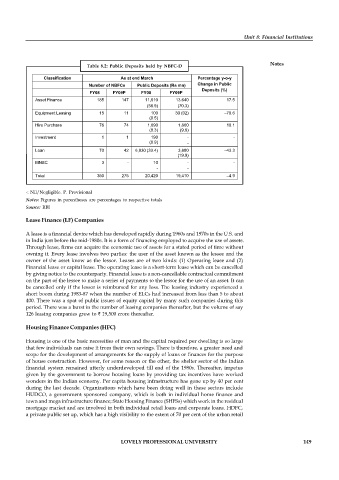
Table 8.2: Public Deposits held by NBFC-D
Classification As at end March Percentage y-o-y
Number of NBFCs Public Deposits (Rs mn) Change in Public
Deposits (%)
FY08 FY09P FY08 FY09P
Asset Finance 185 147 11,610 13.640 17.5
(56.9) (70.3)
Equipment Leasing 15 11 100 30 (02) –70.6
(0.5)
Hire Purchase 76 74 1,690 1,860 10.1
(8.3) (9.6)
Investment 1 1 190 - -
(0.9) -
Loan 70 42 6,830 (33.4) 3,880 –43.3
(19.9)
MNBC 3 - 10 - -
- -
Total 350 275 20,420 19,410 –4.9
-: Nil/Negligible. P. Provisional
Notes: Figures in parentheses are percentages to respective totals
Source: RBI
Lease Finance (LF) Companies
A lease is a financial device which has developed rapidly during 1960s and 1970s in the U.S. and
in India just before the mid-1980s. It is a form of financing employed to acquire the use of assets.
Through lease, firms can acquire the economic use of assets for a stated period of time without
owning it. Every lease involves two parties: the user of the asset known as the lessee and the
owner of the asset know as the lessor. Leases are of two kinds: (1) Operating lease and (2)
Financial lease or capital lease. The operating lease is a short-term lease which can be cancelled
by giving notice to the counterparty. Financial lease is a non-cancellable contractual commitment
on the part of the lessee to make a series of payments to the lessor for the use of an asset. It can
be cancelled only if the lessor is reimbursed for any loss. The leasing industry experienced a
short boom during 1983-87 when the number of ELCs had increased from less than 5 to about
400. There was a spat of public issues of equity capital by many such companies during this
period. There was a burst in the number of leasing companies thereafter, but the volume of say
126 leasing companies grew to ` 19,500 crore thereafter.
Housing Finance Companies (HFC)
Housing is one of the basic necessities of man and the capital required per dwelling is so large
that few individuals can raise it from their own savings. There is therefore, a greater need and
scope for the development of arrangements for the supply of loans or finances for the purpose
of house construction. However, for some reason or the other, the shelter sector of the Indian
financial system remained utterly underdeveloped till end of the 1980s. Thereafter, impetus
given by the government to borrow housing loans by providing tax incentives have worked
wonders in the Indian economy. Per capita housing infrastructure has gone up by 40 per cent
during the last decade. Organizations which have been doing well in these sectors include
HUDCO, a government sponsored company, which is both in individual home finance and
town and mega infrastructure finance; State Housing Finance (SHFSs) which work in the residual
mortgage market and are involved in both individual retail loans and corporate loans. HDFC,
a private public set up, which has a high visibility to the extent of 70 per cent of the urban retail
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 149