Page 76 - DMGT405_FINANCIAL%20MANAGEMENT
P. 76
Financial Management
Notes 5.2.2 Probability Distribution
Probability distribution provides a more quantitative insight into an assets risk. The probability
of a given charge is its chance of occurring.
Notes An outcome with probability of 80% occurrence is expected 8 out of 10 times. An
outcome with probability of 100% is certain to happen. Outcomes with probability of zero
will never occur.
A probability distribution is a model that relates probabilities to the associated outcomes. The
simplest type of probability distribution is the bar chart, which only shows a limited number of
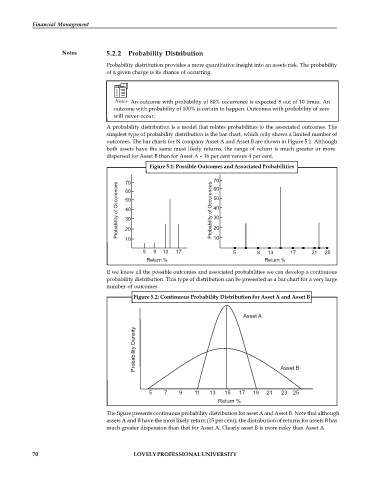
outcomes. The bar charts for N company Asset A and Asset B are shown in Figure 5.1. Although
both assets have the same must likely returns, the range of return is much greater or more
dispersed for Asset B than for Asset A – 16 per cent versus 4 per cent.
Figure 5.1: Possible Outcomes and Associated Probabilities
70
Probability of Occurences 60 Probability of Occurences 70
60
50
50
40
40
30
30
20
20
10
5 9 13 17 10 5 9 13 17 21 25
Return % Return %
If we know all the possible outcomes and associated probabilities we can develop a continuous
probability distribution. This type of distribution can be presented as a bar chart for a very large
number of outcomes.
Figure 5.2: Continuous Probability Distribution for Asset A and Asset B
Asset A
Probability Density Asset B
5 7 9 11 13 15 17 19 21 23 25
Return %
The figure presents continuous probability distribution for asset A and Asset B. Note that although
assets A and B have the most likely return (15 per cent), the distribution of returns for assets B has
much greater dispension than that for Asset A. Clearly asset B is more risky than Asset A.
70 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY