Page 152 - DCOM309_INSURANCE_LAWS_AND_PRACTICES
P. 152
Unit 8: Life Insurance
Notes
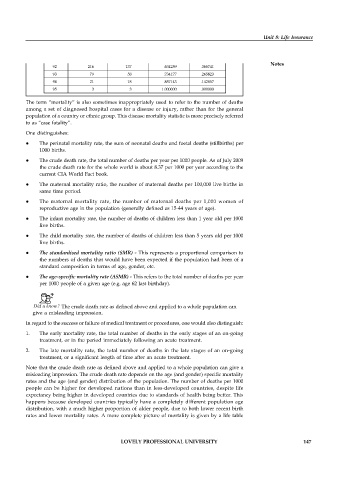
92 216 137 .634259 .365741
93 79 58 .734177 .265823
94 21 18 .857143 .142857
95 3 3 1.000000 .000000
The term “mortality” is also sometimes inappropriately used to refer to the number of deaths
among a set of diagnosed hospital cases for a disease or injury, rather than for the general
population of a country or ethnic group. This disease mortality statistic is more precisely referred
to as “case fatality”.
One distinguishes:
The perinatal mortality rate, the sum of neonatal deaths and foetal deaths (stillbirths) per
1000 births.
The crude death rate, the total number of deaths per year per 1000 people. As of July 2009
the crude death rate for the whole world is about 8.37 per 1000 per year according to the
current CIA World Fact book.
The maternal mortality ratio, the number of maternal deaths per 100,000 live births in
same time period.
The maternal mortality rate, the number of maternal deaths per 1,000 women of
reproductive age in the population (generally defined as 15-44 years of age).
The infant mortality rate, the number of deaths of children less than 1 year old per 1000
live births.
The child mortality rate, the number of deaths of children less than 5 years old per 1000
live births.
The standardised mortality ratio (SMR) - This represents a proportional comparison to
the numbers of deaths that would have been expected if the population had been of a
standard composition in terms of age, gender, etc.
The age-specific mortality rate (ASMR) - This refers to the total number of deaths per year
per 1000 people of a given age (e.g. age 62 last birthday).
Did u know? The crude death rate as defined above and applied to a whole population can
give a misleading impression.
In regard to the success or failure of medical treatment or procedures, one would also distinguish:
1. The early mortality rate, the total number of deaths in the early stages of an on-going
treatment, or in the period immediately following an acute treatment.
2. The late mortality rate, the total number of deaths in the late stages of an on-going
treatment, or a significant length of time after an acute treatment.
Note that the crude death rate as defined above and applied to a whole population can give a
misleading impression. The crude death rate depends on the age (and gender) specific mortality
rates and the age (and gender) distribution of the population. The number of deaths per 1000
people can be higher for developed nations than in less-developed countries, despite life
expectancy being higher in developed countries due to standards of health being better. This
happens because developed countries typically have a completely different population age
distribution, with a much higher proportion of older people, due to both lower recent birth
rates and lower mortality rates. A more complete picture of mortality is given by a life table
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 147