Page 121 - DMGT401Business Environment
P. 121
Business Environment
Notes 5.4.2 Supply of Money, Interest Rate and Investment
The supply of money also has an impact on interest rates and level of investment. In fact,
economists have propounded the theory that to boost development and to create employment,
the government should expand money.
Here too, the fundamentals are the same. As supply of money increases its value goes down. The
price of money is its interest rate. So when banks get more money, they provide loans at low
rates. This increases the level of investment in the country because more people go for investments
with low interest rates. This results in creation of employment, which results in an increase in
purchasing power. This in turn, increases demand and results in inflation, which again works as
a catalyst for investment.
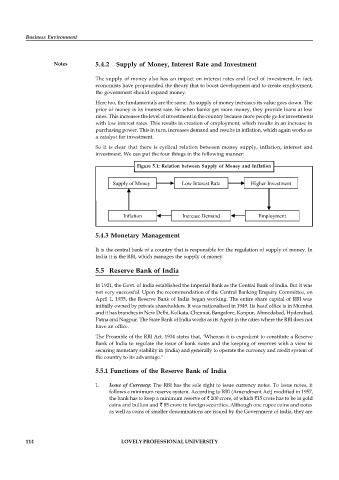
So it is clear that there is cyclical relation between money supply, inflation, interest and
investment. We can put the four things in the following manner:
Figure 5.1: Relation between Supply of Money and Inflation
Supply of Money Low Interest Rate Higher Investment
Inflation Increase Demand Employment
5.4.3 Monetary Management
It is the central bank of a country that is responsible for the regulation of supply of money. In
India it is the RBI, which manages the supply of money.
5.5 Reserve Bank of India
In 1921, the Govt. of India established the Imperial Bank as the Central Bank of India. But it was
not very successful. Upon the recommendation of the Central Banking Enquiry Committee, on
April 1, 1935, the Reserve Bank of India began working. The entire share capital of RBI was
initially owned by private shareholders. It was nationalised in 1949. Its head office is in Mumbai
and it has branches in New Delhi, Kolkata, Chennai, Bangalore, Kanpur, Ahmedabad, Hyderabad,
Patna and Nagpur. The State Bank of India works as its Agent in the cities where the RBI does not
have an office.
The Preamble of the RBI Act, 1934 states that, "Whereas it is expedient to constitute a Reserve
Bank of India to regulate the issue of bank notes and the keeping of reserves with a view to
securing monetary stability in (India) and generally to operate the currency and credit system of
the country to its advantage."
5.5.1 Functions of the Reserve Bank of India
1. Issue of Currency: The RBI has the sole right to issue currency notes. To issue notes, it
follows a minimum reserve system. According to RBI (Amendment Act) modified in 1957,
the bank has to keep a minimum reserve of 200 crore, of which 15 crore has to be in gold
coins and bullion and 85 crore in foreign securities. Although one rupee coins and notes
as well as coins of smaller denominations are issued by the Government of India, they are
114 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY