Page 147 - DMGT401Business Environment
P. 147
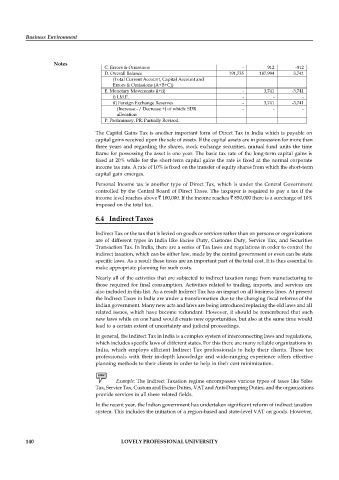
700
13,054
b) Transfers
59
115
i) Official
-56
585
ii) Private
13,110
13,695
5,504
2,855
c) Income
-2,649
2,628
5,042
-2,414
i) Investment Income
227
-235
ii) Compensation of Employees
462
96,451
Total Current Account (I+II)
B. CAPITAL ACCOUNT
52,635
44,880
1. Foreign Investment (a+b)
7,755
8,569
5,419
3,150
a) Foreign Direct Investment (i+ii)
i. In India
8,275
2,302
5,973
2,278
3,713
Equity
5,991
0
Reinvested Earnings
2,166
2,166
Other Capital
24
118
94
ii. Abroad
3,117
-2,823
294
1,914
294
Equity
-1,620
271
-271
Reinvested Earnings
0
0
Other Capital
-932
932
44,066
39,461
4,605
b) Portfolio Investment
In India of which
43,972
39,320
4,652
3,538
42,858
39,320
FIIs
-
ADRs/GDRs
1,114
1,114
Abroad
-47
94
141
10,586
2.Loans (a+b+c)
24,696
14,110
2,336
3,090
754
a) External Assistance
-6
20
i) By India
14
2,342
3,076
734
ii) To India
b) Commercial Borrowings (MT<)
4,521
1,850
2,671
-58
185
i) By India
243
1,607
2,729
4,336
ii) To India
5,579
c) Short Term to India
11,506
17,085
4,073
11,506
i) Suppliers' Credit >180days & Buyers'
15,579
Credit 13,754 110,183 -13,732
ii) Suppliers' Credit up to180 days 1,506 - 1,506
3. Banking Capital (a+b) 16,747 12,742 4,005
a) Commercial Banks 16,745 12,718 4,027
i) Assets 3,263 2,558 705
ii) Liabilities of which: 13,482 10,160 3,322
Business Environment Non-Resident Deposits 11,254 10,133 1,121
b) Others 2 24 -22
4. Rupee Debt Service - 16 -16
5. Other Capital 1,206 5,151 -3,945
Total Capital Account (1 to 5) 95,284 76,899 18,385
Notes
C. Errors & Omissions - 912 -912
D. Overall Balance 191,735 187,994 3,741
(Total Current Account, Capital Account and
Errors & Omissions (A+B+C))
E. Monetary Movements (i+ii) - 3,741 -3,741
i) I.M.F. - - -
ii) Foreign Exchange Reserves - 3,741 -3,741
(Increase - / Decrease +) of which: SDR - - -
allocation
P: Preliminary. PR: Partially Revised.
The Capital Gains Tax is another important form of Direct Tax in India which is payable on
capital gains received upon the sale of assets. If the capital assets are in possession for more than
three years and regarding the shares, stock exchange securities, mutual fund units the time
frame for possessing the asset is one year. The basic tax rate of the long-term capital gains is
fixed at 20% while for the short-term capital gains the rate is fixed at the normal corporate
income tax rate. A rate of 10% is fixed on the transfer of equity shares from which the short-term
capital gain emerges.
Personal Income tax is another type of Direct Tax, which is under the Central Government
controlled by the Central Board of Direct Taxes. The taxpayer is required to pay a tax if the
income level reaches above 100,000. If the income reaches 850,000 there is a surcharge of 10%
imposed on the total tax.
6.4 Indirect Taxes
Indirect Tax or the tax that is levied on goods or services rather than on persons or organizations
are of different types in India like Excise Duty, Customs Duty, Service Tax, and Securities
Transaction Tax. In India, there are a series of Tax laws and regulations in order to control the
indirect taxation, which can be either law, made by the central government or even can be state
specific laws. As a result these taxes are an important part of the total cost. It is thus essential to
make appropriate planning for such costs.
Nearly all of the activities that are subjected to indirect taxation range from manufacturing to
those required for final consumption. Activities related to trading, imports, and services are
also included in this list. As a result Indirect Tax has an impact on all business lines. At present
the Indirect Taxes in India are under a transformation due to the changing fiscal reforms of the
Indian government. Many new acts and laws are being introduced replacing the old laws and all
related issues, which have become redundant. However, it should be remembered that such
new laws while on one hand would create new opportunities, but also at the same time would
lead to a certain extent of uncertainty and judicial proceedings.
In general, the Indirect Tax in India is a complex system of interconnecting laws and regulations,
which includes specific laws of different states. For this there are many reliable organizations in
India, which employs efficient Indirect Tax professionals to help their clients. These tax
professionals with their in-depth knowledge and wide-ranging experience offers effective
planning methods to their clients in order to help in their cost minimization.
Example: The Indirect Taxation regime encompasses various types of taxes like Sales
Tax, Service Tax, Custom and Excise Duties, VAT and Anti-Dumping Duties, and the organizations
provide services in all these related fields.
In the recent year, the Indian government has undertaken significant reform of indirect taxation
system. This includes the initiation of a region-based and state-level VAT on goods. However,
140 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY