Page 89 - DMGT401Business Environment
P. 89
Business Environment
Notes Besides this, the Indian economy is characterised by a high rate of unemployment, scarcity of
capital, fiscal imbalances, balance of payment disequilibria, inflation, and technological
backwardness.
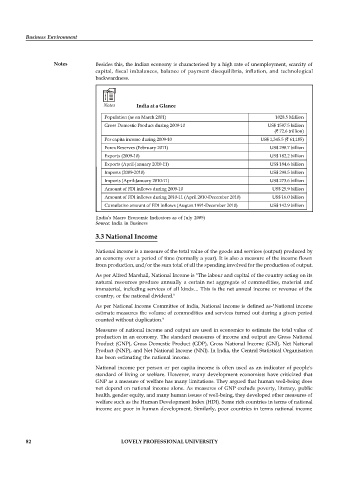
Notes India at a Glance
Population (as on March 2001) 1028.5 Million
Gross Domestic Product during 2009-10 US$ 1597.5 billion
( 72.6 trillion)
Per capita income during 2009-10 US$ 1,345.5 ( 61,185)
Forex Reserves (February 2011) US$ 298.7 billion
Exports (2009-10) US$ 182.2 billion
Exports (April-January 2010-11) US$ 184.6 billion
Imports (2009-2010) US$ 299.5 billion
Imports (April-January 2010-11) US$ 273.6 billion
Amount of FDI inflows during 2009-10 US$ 25.9 billion
Amount of FDI inflows during 2010-11 (April 2010-December 2010) US$ 16.0 billion
Cumulative amount of FDI Inflows (August 1991-December 2010) US$ 142.9 billion
(India’s Macro Economic Indicators as of July 2005)
Source: India in Business
3.3 National Income
National income is a measure of the total value of the goods and services (output) produced by
an economy over a period of time (normally a year). It is also a measure of the income flown
from production, and/or the sum total of all the spending involved for the production of output.
As per Alfred Marshall, National Income is "The labour and capital of the country acting on its
natural resources produce annually a certain net aggregate of commodities, material and
immaterial, including services of all kinds… This is the net annual income or revenue of the
country, or the national dividend."
As per National Income Committee of India, National Income is defined as-"National income
estimate measures the volume of commodities and services turned out during a given period
counted without duplication."
Measures of national income and output are used in economics to estimate the total value of
production in an economy. The standard measures of income and output are Gross National
Product (GNP), Gross Domestic Product (GDP), Gross National Income (GNI), Net National
Product (NNP), and Net National Income (NNI). In India, the Central Statistical Organisation
has been estimating the national income.
National income per person or per capita income is often used as an indicator of people's
standard of living or welfare. However, many development economists have criticized that
GNP as a measure of welfare has many limitations. They argued that human well-being does
not depend on national income alone. As measures of GNP exclude poverty, literacy, public
health, gender equity, and many human issues of well-being, they developed other measures of
welfare such as the Human Development Index (HDI). Some rich countries in terms of national
income are poor in human development. Similarly, poor countries in terms national income
82 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY