Page 192 - DCOM302_MANAGEMENT_ACCOUNTING
P. 192
Unit 9: Variance Analysis
Likewise, the efficiency could be denominated in terms of units of production. If the actual Notes
production is more than that of the standard production in units, the firm is favourable in
position in producing the articles than the standard.
Overhead Efficiency Variance = (Actual Production in Units – Standard Production in
Units) × Standard Rate
= (9,200 units – 8,750 units) .30
= 450 units .30
= 135 (Favourable)
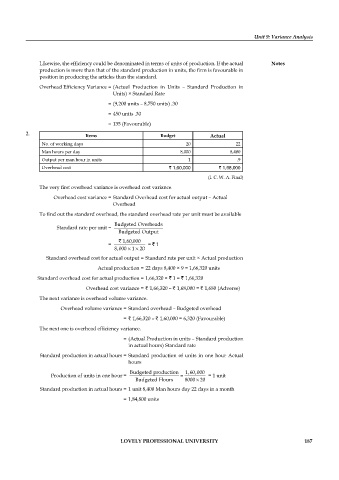
2. Items Budget Actual
No. of working days 20 22
Man hours per day 8,000 8,400
Output per man hour in units 1 .9
Overhead cost ` 1,60,000 ` 1,68,000
(I. C. W. A. Final)
The very first overhead variance is overhead cost variance.
Overhead cost variance = Standard Overhead cost for actual output – Actual
Overhead
To find out the standard overhead, the standard overhead rate per unit must be available
Budgeted Overheads
Standard rate per unit =
Budgeted Output
` 1,60,000
= = ` 1
8,000 ×× 20
1
Standard overhead cost for actual output = Standard rate per unit × Actual production
Actual production = 22 days 8,400 × 9 = 1,66,320 units
Standard overhead cost for actual production = 1,66,320 × ` 1 = ` 1,66,320
Overhead cost variance = ` 1,66,320 – ` 1,68,000 = ` 1,680 (Adverse)
The next variance is overhead volume variance.
Overhead volume variance = Standard overhead – Budgeted overhead
= ` 1,66,320 – ` 1,60,000 = 6,320 (Favourable)
The next one is overhead effi ciency variance.
= (Actual Production in units – Standard production
in actual hours) Standard rate
Standard production in actual hours = Standard production of units in one hour Actual
hours
Budgeted production 1,60,000
Production of units in one hour = = = 1 unit
×
Budgeted Hours 8000 20
Standard production in actual hours = 1 unit 8,400 Man hours day 22 days in a month
= 1,84,800 units
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 187