Page 199 - DCOM302_MANAGEMENT_ACCOUNTING
P. 199
Management Accounting
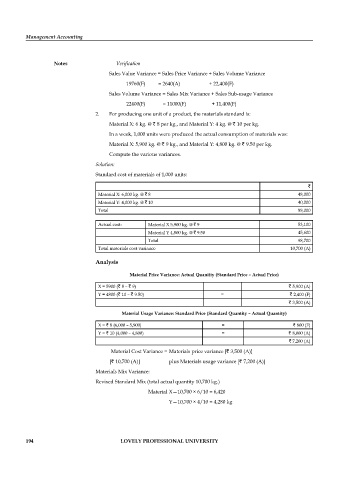
Notes Verifi cation
Sales Value Variance = Sales Price Variance + Sales Volume Variance
19760(F) = 2640(A) + 22,400(F)
Sales Volume Variance = Sales Mix Variance + Sales Sub-usage Variance
22400(F) = 11000(F) + 11,400(F)
2. For producing one unit of a product, the materials standard is:
Material X: 6 kg. @ ` 8 per kg., and Material Y: 4 kg. @ ` 10 per kg.
In a week, 1,000 units were produced the actual consumption of materials was:
Material X: 5,900 kg. @ ` 9 kg., and Material Y: 4,800 kg. @ ` 9.50 per kg.
Compute the various variances.
Solution:
Standard cost of materials of 1,000 units:
`
Material X: 6,000 kg. @ ` 8 48,000
Material Y: 4,000 kg. @ ` 10 40,000
Total 88,000
Actual cost: Material X 5,900 kg. @ ` 9 53,100
Material Y 4,800 kg. @ ` 9.50 45,600
Total 98,700
Total materials cost variance 10,700 (A)
Analysis
Material Price Variance: Actual Quantity (Standard Price – Actual Price)
X = 5900 (` 8 – ` 9) ` 5,900 (A)
Y = 4800 (` 10 – ` 9.50) = ` 2,400 (F)
` 3,500 (A)
Material Usage Variance: Standard Price (Standard Quantity – Actual Quantity)
X = ` 8 (6,000 – 5,900) = ` 800 (F)
Y = ` 10 (4,000 – 4,800) = ` 8,000 (A)
` 7,200 (A)
Material Cost Variance = Materials price variance [` 3,500 (A)]
[` 10,700 (A)] plus Materials usage variance [` 7,200 (A)]
Materials Mix Variance:
Revised Standard Mix (total actual quantity 10,700 kg.)
Material X—10,700 × 6/10 = 6,420
Y—10,700 × 4/10 = 4,280 kg
194 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY