Page 140 - DECO405_MANAGERIAL_ECONOMICS
P. 140
Unit 8: Cost Analysis
Notes
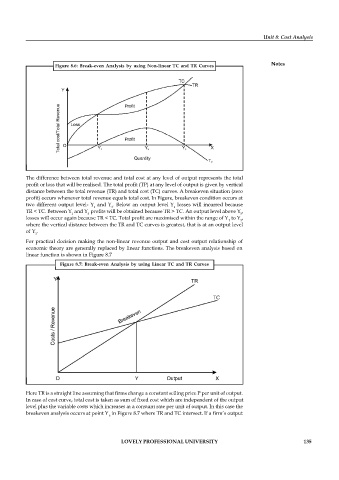
Figure 8.6: Break-even Analysis by using Non-linear TC and TR Curves
The difference between total revenue and total cost at any level of output represents the total
profit or loss that will be realised. The total profit (TP) at any level of output is given by vertical
distance between the total revenue (TR) and total cost (TC) curves. A breakeven situation (zero
profit) occurs whenever total revenue equals total cost. In Figure, breakeven condition occurs at
two different output level- Y and Y . Below an output level Y losses will incurred because
1 3 1
TR < TC. Between Y and Y profits will be obtained because TR > TC. An output level above Y ,
1 3 3
losses will occur again because TR < TC. Total profit are maximised within the range of Y to Y ,
1 3
where the vertical distance between the TR and TC curves is greatest, that is at an output level
of Y .
2
For practical decision making the non-linear revenue output and cost output relationship of
economic theory are generally replaced by linear functions. The breakeven analysis based on
linear function is shown in Figure 8.7
Figure 8.7: Break-even Analysis by using Linear TC and TR Curves
Here TR is a straight line assuming that firms change a constant selling price P per unit of output.
In case of cost curve, total cost is taken as sum of fixed cost which are independent of the output
level plus the variable costs which increases at a constant rate per unit of output. In this case the
breakeven analysis occurs at point Y in Figure 8.7 where TR and TC intersect. If a firm’s output
b
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 135