Page 205 - DECO405_MANAGERIAL_ECONOMICS
P. 205
Managerial Economics
Notes (c) Under oligopoly, a firm expects that when it raises its price, it is most likely that
rival firms will also ....................... the price.
(d) For an oligopolistic firm, the demand curve is highly ....................... and gradually
falling for prices above the current or existing price.
(e) Sweezy's kinked demand curve model explains the rigidity or stickiness in
oligopolistic prices in the face of short-term increases or decreases in .......................
input costs.
(f) The Hall and Hitch model of the Kinked demand curve is based on an empirical
survey of a sample of 38 well managed firms in ....................... .
2. State true or false for the following statements:
(a) Locational advantages and managerial talents have nothing to do with entry barriers.
(b) Price leadership can be seen as collusive oligopoly.
(c) Under oligopoly, new entry is easy.
(d) The demand curve of an oligopolist is indeterminate.
(e) Under Hall and Hitch version the demand curve has a kink at the price which is
above full cost price.
(f) Oligopoly firm may form cartel.
(g) Price leadership is, where firms jointly fix a price and output through agreement.
12.10 Review Questions
1. In what form does rivalry occur in an oligopoly? Why does competition among rivals
occur most often in oliogopolies?
2. Why is there so much advertising in oligopoly? How does such advertising help consumers
and promote efficiency? Why might it be expensive at times?
3. ‘Oligopoly is the most prevalent form of market structure in the manufacturing sector’.
Describe this statement with the help of an example.
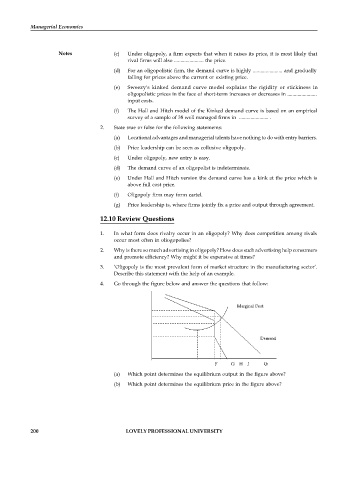
4. Go through the figure below and answer the questions that follow:
F G H J Quantity (Q)
(a) Which point determines the equilibrium output in the figure above?
(b) Which point determines the equilibrium price in the figure above?
200 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY