Page 92 - DECO405_MANAGERIAL_ECONOMICS
P. 92
Unit 6: Production Theory
goods and services for sale at a profit. The most important reason for a firm or business enterprises Notes
exist is that firms are specialised organisation devoted to manage the process of production.
6.1 Meaning of Production
Production refers to the transformation of inputs or resources into outputs or goods and services.
Production is a process in which economic resources or inputs (composed of natural resources
like labour, land and capital equipment) are combined by entrepreneurs to create economic
goods and services (outputs or products).
Firms are required to take different but interrelated production decisions like:
1. Whether or not to actually produce or shut down?
2. How much to produce?
3. What input combination to use?
4. What type of technology to use?
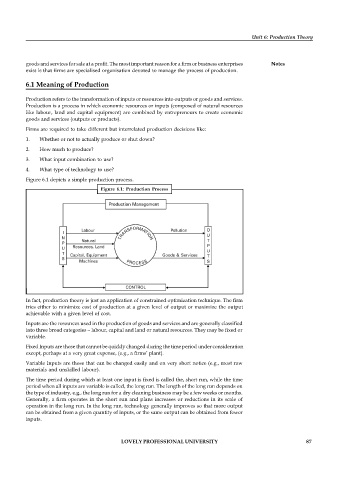
Figure 6.1 depicts a simple production process.
Figure 6.1: Production Process
In fact, production theory is just an application of constrained optimization technique. The firm
tries either to minimize cost of production at a given level of output or maximize the output
achievable with a given level of cost.
Inputs are the resources used in the production of goods and services and are generally classified
into three broad categories – labour, capital and land or natural resources. They may be fixed or
variable.
Fixed Inputs are those that cannot be quickly changed during the time period under consideration
except, perhaps at a very great expense, (e.g., a firms’ plant).
Variable Inputs are those that can be changed easily and on very short notice (e.g., most raw
materials and unskilled labour).
The time period during which at least one input is fixed is called the, short run, while the time
period when all inputs are variable is called, the long run. The length of the long run depends on
the type of industry, e.g., the long run for a dry cleaning business may be a few weeks or months.
Generally, a firm operates in the short run and plans increases or reductions in its scale of
operation in the long run. In the long run, technology generally improves so that more output
can be obtained from a given quantity of inputs, or the same output can be obtained from fewer
inputs.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 87