Page 95 - DCOM409_CONTEMPORARY_ACCOUNTING
P. 95
Contemporary Accounting
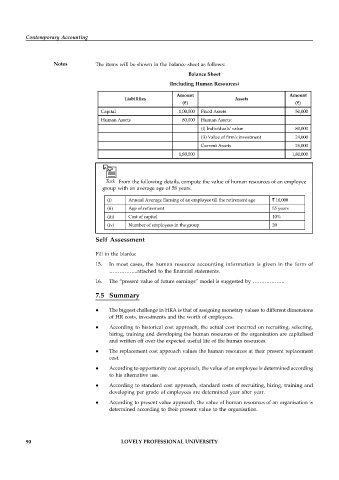
Notes The items will be shown in the balance sheet as follows:
Balance Sheet
(Including Human Resources)
Amount Amount
Liabilities Assets
(`) (`)
Capital 1,00,000 Fixed Assets 50,000
Human Assets 80,000 Human Assets:
(i) Individuals' value 80,000
(ii) Value of firm's investment 24,000
Current Assets 26,000
1,80,000 1,80,000
Task From the following details, compute the value of human resources of an employee
group with an average age of 58 years.
(i) Annual Average Earning of an employee till the retirement age ` 10,000
(ii) Age of retirement 55 years
(iii) Cost of capital 10%
(iv) Number of employees in the group 20
Self Assessment
Fill in the blanks:
15. In most cases, the human resource accounting information is given in the form of
……………..attached to the financial statements.
16. The “present value of future earnings” model is suggested by ……………….
7.5 Summary
The biggest challenge in HRA is that of assigning monetary values to different dimensions
of HR costs, investments and the worth of employees.
According to historical cost approach, the actual cost incurred on recruiting, selecting,
hiring, training and developing the human resources of the organisation are capitalised
and written off over the expected useful life of the human resources.
The replacement cost approach values the human resources at their present replacement
cost.
According to opportunity cost approach, the value of an employee is determined according
to his alternative use.
According to standard cost approach, standard costs of recruiting, hiring, training and
developing per grade of employees are determined year after year.
According to present value approach, the value of human resources of an organisation is
determined according to their present value to the organisation.
90 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY