Page 11 - DCOM304_INDIAN_FINANCIAL_SYSTEM
P. 11
Indian Financial System
Notes interest bearing assets. The claims issued by the DSUs are called direct claims and are
typically sold in financial markets. For example, if Tata Motors needs to borrow money to
fund building a car manufacturing plant, it might borrow the money from savers by
selling the bonds, a debt security that promises to make payment periodically for a specified
period of time. Direct financing allows SSUs an outlet for their savings, which provides an
expected return and DSUs no longer needs to defer current consumption or promising
investment opportunities for lack of funds. However, one problem involved in direct
financing is that DSUs must scout SSUs that want primary claims with precisely the
characteristics they can and are willing to sell. To aid in the search process there exists a
number of market specialists such brokers who act purely as 'matchmakers' between SSUs
and DSUs and charge a commission for their services. Dealers also provide search services
and make markets in securities by maintaining an inventory from which they buy and sell
for profit. They derive their income from providing search services and from the spread
earned on the buying and selling price of securities held in inventory. Another market
specialist is the underwriter who helps DSUs bring their financial claims to market.
Underwriters primarily perform risk bearing function. They buy the entire block of
securities to be issued by a DSU at a guaranteed price and then resell the securities to
individual investors. Income of the underwriters is the spread between the fixed price
paid for securities and the price at which they are resold in the open market. The bottom
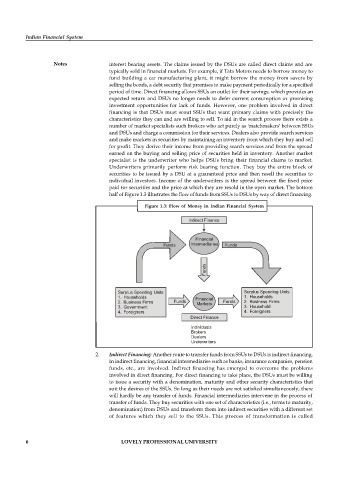
half of Figure 1.3 illustrates the flow of funds from SSUs to DSUs by way of direct financing.
Figure 1.3: Flow of Money in Indian Financial System
Indirect Finance
Financial
Funds Intermediaries Funds
Funds
Surplus Spending Units Surplus Spending Units
1. Households Financial 1. Households
2. Business Firms Funds Markets Funds 2. Business Firms
3. Government 3. Household
4. Foreigners 4. Foreigners
Direct Finance
Individuals
Brokers
Dealers
Underwriters
2. Indirect Financing: Another route to transfer funds from SSUs to DSUs is indirect financing.
In indirect financing, financial intermediaries such as banks, insurance companies, pension
funds, etc., are involved. Indirect financing has emerged to overcome the problems
involved in direct financing. For direct financing to take place, the DSUs must be willing
to issue a security with a denomination, maturity and other security characteristics that
suit the desires of the SSUs. So long as their needs are not satisfied simultaneously, there
will hardly be any transfer of funds. Financial intermediaries intervene in the process of
transfer of funds. They buy securities with one set of characteristics (i.e., terms to maturity,
denomination) from DSUs and transform them into indirect securities with a different set
of features which they sell to the SSUs. This process of transformation is called
6 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY