Page 152 - DCOM304_INDIAN_FINANCIAL_SYSTEM
P. 152
Unit 8: Financial Institutions
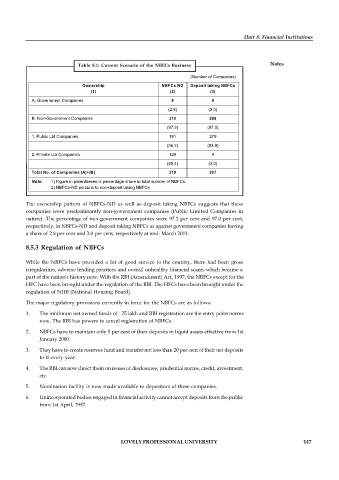
Table 8.1: Current Scenario of the NBFCs Business Notes
(Number of Companies)
Ownership NBFCs ND Deposit taking NBFCs
(1) (2) (3)
A. Government Companies 9 9
(2.8) (3.0)
B. Non-Government Companies 310 288
(97.2) (97.0)
1. Public Ltd Companies 181 279
(56.7) (93.9)
2. Private Ltd Companies 129 9
(40.4) (3.0)
Total No. of Companies (A)+(B) 319 297
Note: 1) Figure in parentheses is percentage share in total number of NBFCs.
2) NBFCs-ND pertains to non-deposit taking NBFCs
The ownership pattern of NBFCs-ND as well as deposit taking NBFCs suggests that these
companies were predominantly non-government companies (Public Limited Companies in
nature). The percentage of non-government companies were 97.2 per cent and 97.0 per cent,
respectively, in NBFCs-ND and deposit taking NBFCs as against government companies having
a share of 2.8 per cent and 3.0 per cent, respectively at end- March 2011.
8.5.3 Regulation of NBFCs
While the NBFCs have provided a lot of good service to the country, there had been gross
irregularities, adverse lending practices and overall unhealthy financial scams which became a
part of the nation's history now. With the RBI (Amendment) Act, 1997, the NBFCs except for the
HFC have been brought under the regulation of the RBI. The HFCs have been brought under the
regulation of NHB (National Housing Board).
The major regulatory provisions currently in force for the NBFCs are as follows:
1. The minimum net owned funds of ` 25 lakh and RBI registration are the entry point norms
now. The RBI has powers to cancel registration of NBFCs.
2. NBFCs have to maintain only 5 per cent of their deposits in liquid assets effective from 1st
January 2000.
3. They have to create reserves fund and transfer not less than 20 per cent of their net deposits
to it every year.
4. The RBI can now direct them on issues of disclosures, prudential norms, credit, investment,
etc.
5. Nomination facility is now made available to depositors of these companies.
6. Unincorporated bodies engaged in financial activity cannot accept deposits from the public
from 1st April, 1997.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 147