Page 48 - DCOM304_INDIAN_FINANCIAL_SYSTEM
P. 48
Unit 3: Financial Markets
Notes
Notes In India, two types of repos are in vogue, viz., interbank repos and the RBI repos.
Interbank repos are permitted under regulated conditions. After the detection of the
irregularities in securities transactions in 1992, eligible participants and instruments were
restricted but subsequently liberalised in a gradual manner. The Reserve Bank repos are
used for absorption/injection of liquidity.
Banks and primary dealers are allowed to undertake both repo/reverse repo transactions.
Non-bank participants have also been allowed recently to lend money through reverse
repos to other eligible participants. The RBI has lately removed the restriction of a
minimum period of 3 days for interbank repo transactions. This will help the banks and
other participants in the repo market to adjust their liquidity in a more flexible manner.
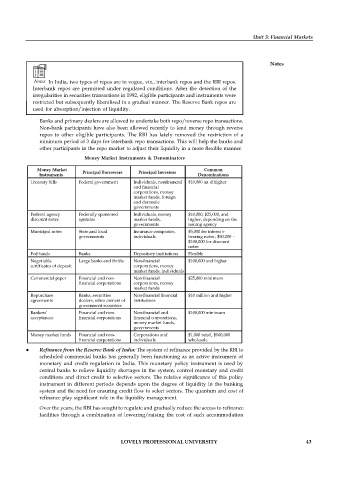
Money Market Instruments & Denominators
Money Market Principal Borrowers Principal Investors Common
Instruments Denominations
-
Treasury bills Federal government Individuals, nonfinancial $10,000 an d higher
and financial
corporations, money
market funds, foreign
and domestic
governments
Federal agency Federally sponsored Individuals, money $10,000, $25,000, and
discount notes agencies market funds, higher, depending on the
governments issuing agency
Municipal notes State and local Insurance companies, $5,000 for interes t-
governments individuals bearing notes; $50,000 -
$100,000 for discount
notes
Fed funds Banks Depository institutions Flexible
Negotiable Large banks and thrifts Non-financial $100,000 and higher
certificates of deposit corporations, money
market funds, individuals
Commercial paper Financial and non- Non-financial $25,000 minimum
financial corporations corporations, money
market funds
Repurchase Banks, securities Non-financial financial $10 million and higher
agreements dealers, other owners of institutions
government securities
Bankers’ Financial and non- Non-financial and $100,000 minimum
acceptances financial corporations financial corporations,
money market funds,
governments
Money market funds Financial and non- Corporations and $1,000 retail, $100,000
financial corporations individuals wholesale
Refinance from the Reserve Bank of India: The system of refinance provided by the RBI to
scheduled commercial banks has generally been functioning as an active instrument of
monetary and credit regulation in India. This monetary policy instrument is used by
central banks to relieve liquidity shortages in the system, control monetary and credit
conditions and direct credit to selective sectors. The relative significance of this policy
instrument in different periods depends upon the degree of liquidity in the banking
system and the need for ensuring credit flow to select sectors. The quantum and cost of
refinance play significant role in the liquidity management.
Over the years, the RBI has sought to regulate and gradually reduce the access to refinance
facilities through a combination of lowering/raising the cost of such accommodation
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 43