Page 26 - DCOM505_WORKING_CAPITAL_MANAGEMENT
P. 26
Unit 2: Planning of Working Capital
Notes
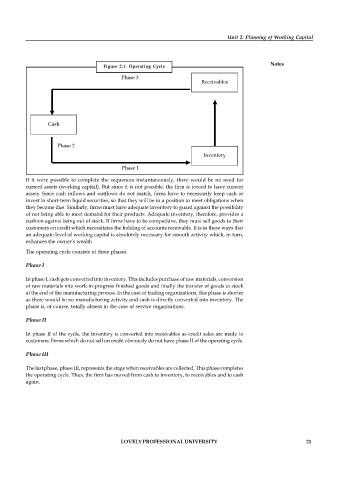
Figure 2.1: Operating Cycle
Phase 3
Receivables
Cash
Phase 2
Inventory
Phase 1
If it were possible to complete the sequences instantaneously, there would be no need for
current assets (working capital). But since it is not possible, the firm is forced to have current
assets. Since cash inflows and outflows do not match, firms have to necessarily keep cash or
invest in short-term liquid securities, so that they will be in a position to meet obligations when
they become due. Similarly, firms must have adequate inventory to guard against the possibility
of not being able to meet demand for their products. Adequate inventory, therefore, provides a
cushion against being out of stock. If firms have to be competitive, they must sell goods to their
customers on credit which necessitates the holding of accounts receivable. It is in these ways that
an adequate level of working capital is absolutely necessary for smooth activity which, in turn,
enhances the owner’s wealth.
The operating cycle consists of three phases.
Phase I
In phase I, cash gets converted into inventory. This includes purchase of raw materials, conversion
of raw materials into work-in-progress finished goods and finally the transfer of goods to stock
at the end of the manufacturing process. In the case of trading organizations, this phase is shorter
as there would be no manufacturing activity and cash is directly converted into inventory. The
phase is, of course, totally absent in the case of service organisations.
Phase II
In phase II of the cycle, the inventory is converted into receivables as credit sales are made to
customers. Firms which do not sell on credit obviously do not have phase II of the operating cycle.
Phase III
The last phase, phase III, represents the stage when receivables are collected. This phase completes
the operating cycle. Thus, the firm has moved from cash to inventory, to receivables and to cash
again.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 21