Page 109 - DCOM510_FINANCIAL_DERIVATIVES
P. 109
Financial Derivatives
Notes Equivalently a long hedge locks in the interest rate of price of a cash security that will be
purchased in the future subject to small adjustment due to the basis risk. A long hedge is also
known as an anticipatory hedge, because it is effectively a substitute position for a future cash
transaction. The pay-off profile of long hedging is depicted in Figure 7.3.
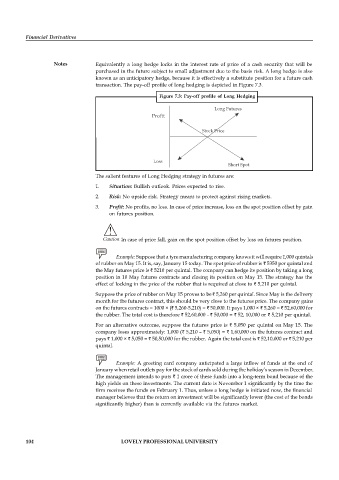
Figure 7.3: Pay-off profile of Long Hedging
Long Futures
Profit
Stock Price
Loss
Short Spot
The salient features of Long Hedging strategy in futures are:
1. Situation: Bullish outlook. Prices expected to rise.
2. Risk: No upside risk. Strategy meant to protect against rising markets.
3. Profit: No profits, no loss. In case of price increase, loss on the spot position offset by gain
on futures position.
!
Caution In case of price fall, gain on the spot position offset by loss on futures position.
Example: Suppose that a tyre manufacturing company knows it will require 1,000 quintals
of rubber on May 15. It is, say, January 15 today. The spot price of rubber is ` 5350 per quintal and
the May futures price is ` 5210 per quintal. The company can hedge its position by taking a long
position in 10 May futures contracts and closing its position on May 15. The strategy has the
effect of locking in the price of the rubber that is required at close to ` 5,210 per quintal.
Suppose the price of rubber on May 15 proves to be ` 5,260 per quintal. Since May is the delivery
month for the futures contract, this should be very close to the futures price. The company gains
on the futures contracts = 1000 × (` 5,260-5,210) = ` 50,000. It pays 1,000 × ` 5,260 = ` 52,60,000 for
the rubber. The total cost is therefore ` 52,60,000 - ` 50,000 = ` 52, 10,000 or ` 5,210 per quintal.
For an alternative outcome, suppose the futures price is ` 5,050 per quintal on May 15. The
company loses approximately: 1,000 (` 5,210 – ` 5,050) = ` 1,60,000 on the futures contract and
pays ` 1,000 × ` 5,050 = ` 50,50,000 for the rubber. Again the total cost is ` 52,10,000 or ` 5,210 per
quintal.
Example: A greeting card company anticipated a large inflow of funds at the end of
January when retail outlets pay for the stock of cards sold during the holiday’s season in December.
The management intends to puts ` 1 crore of these funds into a long-term bond because of the
high yields on these investments. The current date is November 1 significantly by the time the
firm receives the funds on February 1. Thus, unless a long hedge is initiated now, the financial
manager believes that the return on investment will be significantly lower (the cost of the bonds
significantly higher) than is currently available via the futures market.
104 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY