Page 14 - DCOM510_FINANCIAL_DERIVATIVES
P. 14
Unit 1: Introduction to Derivatives
Notes
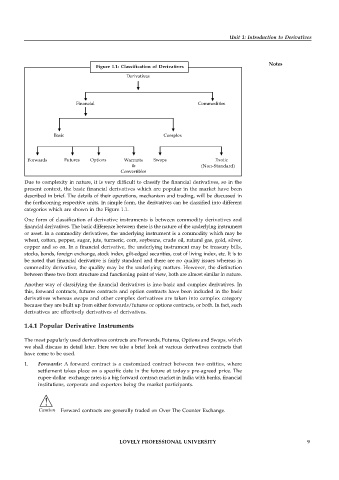
Figure 1.1: Classification of Derivatives
Derivatives
Financial Commodities
Basic Complex
Forwards Futures Options Warrants Swaps Exotic
& (Non-Standard)
(Non – Standard)
Convertibles
Due to complexity in nature, it is very difficult to classify the financial derivatives, so in the
present context, the basic financial derivatives which are popular in the market have been
described in brief. The details of their operations, mechanism and trading, will be discussed in
the forthcoming respective units. In simple form, the derivatives can be classified into different
categories which are shown in the Figure 1.1.
One form of classification of derivative instruments is between commodity derivatives and
financial derivatives. The basic difference between these is the nature of the underlying instrument
or asset. In a commodity derivatives, the underlying instrument is a commodity which may be
wheat, cotton, pepper, sugar, jute, turmeric, corn, soybeans, crude oil, natural gas, gold, silver,
copper and so on. In a financial derivative, the underlying instrument may be treasury bills,
stocks, bonds, foreign exchange, stock index, gilt-edged securities, cost of living index, etc. It is to
be noted that financial derivative is fairly standard and there are no quality issues whereas in
commodity derivative, the quality may be the underlying matters. However, the distinction
between these two from structure and functioning point of view, both are almost similar in nature.
Another way of classifying the financial derivatives is into basic and complex derivatives. In
this, forward contracts, futures contracts and option contracts have been included in the basic
derivatives whereas swaps and other complex derivatives are taken into complex category
because they are built up from either forwards/futures or options contracts, or both. In fact, such
derivatives are effectively derivatives of derivatives.
1.4.1 Popular Derivative Instruments
The most popularly used derivatives contracts are Forwards, Futures, Options and Swaps, which
we shall discuss in detail later. Here we take a brief look at various derivatives contracts that
have come to be used.
1. Forwards: A forward contract is a customized contract between two entities, where
settlement takes place on a specific date in the future at today’s pre-agreed price. The
rupee-dollar exchange rates is a big forward contract market in India with banks, financial
institutions, corporate and exporters being the market participants.
!
Caution Forward contracts are generally traded on Over The Counter Exchange.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 9