Page 199 - DCOM510_FINANCIAL_DERIVATIVES
P. 199
Financial Derivatives
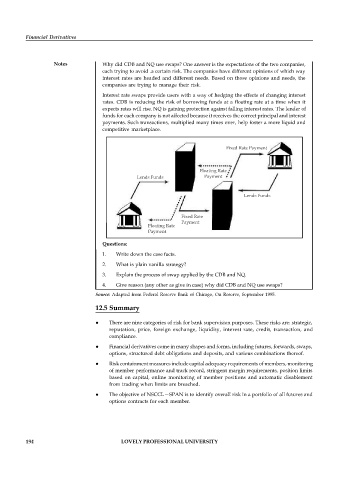
Notes Why did CDB and NQ use swaps? One answer is the expectations of the two companies,
each trying to avoid .a certain risk. The companies have different opinions of which way
interest rates are headed and different needs. Based on those opinions and needs, the
companies are trying to manage their risk.
Interest rate swaps provide users with a way of hedging the effects of changing interest
rates. CDB is reducing the risk of borrowing funds at a floating rate at a time when it
expects rates will rise. NQ is gaining protection against falling interest rates. The lender of
funds for each company is not affected because it receives the correct principal and interest
payments. Such transactions, multiplied many times over, help foster a more liquid and
competitive marketplace.
Fixed Rate Payment
Floating Rate
Lends Funds Payment
Lends Funds
Fixed Rate
Payment
Floating Rate
Payment
Questions:
1. Write down the case facts.
2. What is plain vanilla strategy?
3. Explain the process of swap applied by the CDB and NQ.
4. Give reason (any other as give in case) why did CDB and NQ use swaps?
Source: Adapted from Federal Reserve Bank of Chicago, On Reserve, September 1995.
12.5 Summary
There are nine categories of risk for bank supervision purposes. These risks are: strategic,
reputation, price, foreign exchange, liquidity, interest rate, credit, transaction, and
compliance.
Financial derivatives come in many shapes and forms, including futures, forwards, swaps,
options, structured debt obligations and deposits, and various combinations thereof.
Risk containment measures include capital adequacy requirements of members, monitoring
of member performance and track record, stringent margin requirements, position limits
based on capital, online monitoring of member positions and automatic disablement
from trading when limits are breached.
The objective of NSCCL—SPAN is to identify overall risk in a portfolio of all futures and
options contracts for each member.
194 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY