Page 45 - DCOM510_FINANCIAL_DERIVATIVES
P. 45
Financial Derivatives
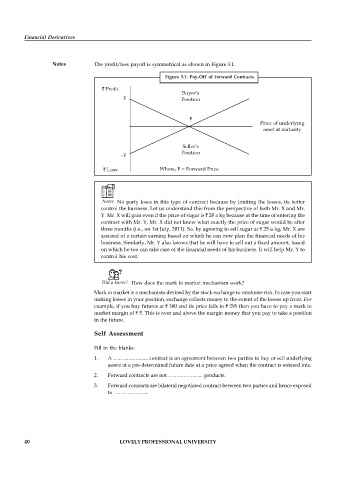
Notes The profit/loss payoff is symmetrical as shown in Figure 3.1.
Figure 3.1: Pay-Off of forward Contracts
` Profit
Buyer’s
F Position
F
Price of underlying
asset at maturity
Seller’s
Position
–F
` Loss Where, F = Forward Price
Notes No party loses in this type of contract because by limiting the losses, its better
control the business. Let us understand this from the perspective of both Mr. X and Mr.
Y. Mr. X will gain even if the price of sugar is ` 20 a kg because at the time of entering the
contract with Mr. Y, Mr. X did not know what exactly the price of sugar would be after
three months (i.e., on 1st July, 2011). So, by agreeing to sell sugar at ` 25 a kg, Mr. X are
assured of a certain earning based on which he can now plan the financial needs of his
business. Similarly, Mr. Y also knows that he will have to sell out a fixed amount, based
on which he too can take care of the financial needs of his business. It will help Mr. Y to
control his cost.
Did u know? How does the mark to market mechanism work?
Mark to market is a mechanism devised by the stock exchange to minimise risk. In case you start
making losses in your position, exchange collects money to the extent of the losses up front. For
example, if you buy futures at ` 300 and its price falls to ` 295 then you have to pay a mark to
market margin of ` 5. This is over and above the margin money that you pay to take a position
in the future.
Self Assessment
Fill in the blanks:
1. A ……………....... contract is an agreement between two parties to buy or sell underlying
assets at a pre-determined future date at a price agreed when the contract is entered into.
2. Forward contracts are not ……………....... products.
3. Forward contracts are bilateral negotiated contract between two parties and hence exposed
to …………….......
40 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY