Page 148 - DCAP210_INTRODUCTION__TO_MICROPROCESSORS
P. 148
Introduction to Microprocessors
Notes 3. When data is loaded using LXI instruction then low-order byte first followed by the high-
order byte where as in MVI high-order byte first followed by the low-order byte.
10.2.2 Data Transfer between Memory and Microprocessor
The 8085 instruction set includes instructions having data transfer:
1. From memory to the microprocessor.
2. From microprocessor to the memory or directly into the memory.
(1) From Memory to the Microprocessor
The 8085 instruction set includes three types of memory transfer instructions. These instructions
do not affect the flags.
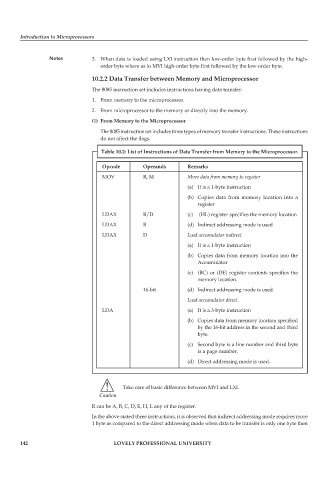
Table 10.2: List of Instructions of Data Transfer from Memory to the Microprocessor.
Opcode Operands Remarks
MOV R, M Move data from memory to register
(a) It is a 1-byte instruction
(b) Copies data from memory location into a
register
LDAX B/D (c) (HL) register specifies the memory location
LDAX B (d) Indirect addressing mode is used
LDAX D Load accumulator indirect
(a) It is a 1-byte instruction
(b) Copies data from memory location into the
Accumulator
(c) (BC) or (DE) register contents specifies the
memory location.
16-bit (d) Indirect addressing mode is used.
Load accumulator direct.
LDA (a) It is a 3-byte instruction
(b) Copies data from memory location specified
by the 16-bit address in the second and third
byte.
(c) Second byte is a line number and third byte
is a page number.
(d) Direct addressing mode is used.
Take care of basic difference between MVI and LXI.
R can be A, B, C, D, E, H, L any of the register.
In the above stated three instructions, it is observed that indirect addressing mode requires more
1 byte as compared to the direct addressing mode when data to be transfer is only one byte then
142 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY