Page 175 - DCAP210_INTRODUCTION__TO_MICROPROCESSORS
P. 175
Unit 12: The Stacks
it back, the next RET instruction will cause a jump to HL, which can be anywhere in the ROM/ Notes
RAM and the computer will crash. Note however, it's also a way to jump to the location stored in
HL, but then you should really use the JMP instruction, to do the same thing. Push and pop
doesn't change any flags, so you can use them between a compare and jump instructions,
depending on a condition, which is often very useful.
12.3.1 The PUSH Instruction
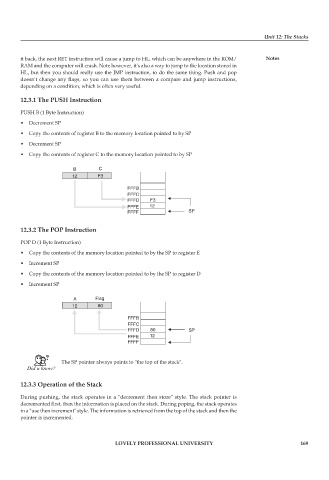
PUSH B (1 Byte Instruction)
• Decrement SP
• Copy the contents of register B to the memory location pointed to by SP
• Decrement SP
• Copy the contents of register C to the memory location pointed to by SP
12.3.2 The POP Instruction
POP D (1 Byte Instruction)
• Copy the contents of the memory location pointed to by the SP to register E
• Increment SP
• Copy the contents of the memory location pointed to by the SP to register D
• Increment SP
The SP pointer always points to "the top of the stack".
12.3.3 Operation of the Stack
During pushing, the stack operates in a "decrement then store" style. The stack pointer is
decremented first, then the information is placed on the stack. During poping, the stack operates
in a "use then increment" style. The information is retrieved from the top of the stack and then the
pointer is incremented.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 169