Page 245 - DCAP310_INTRODUCTION_TO_ARTIFICIAL_INTELLIGENCE_AND_EXPERT_SYSTEMS
P. 245
Unit 13: Expert System Architecture
Conventional computer programs perform tasks using a decision-making logic containing Notes
very little knowledge other than the basic algorithm for solving that specific problem. The basic
knowledge is often embedded as part of the programming code, so that as the knowledge
changes, the program has to be rebuilt.
Did u know? Knowledge-based expert systems collect the small fragments of human
knowhow into a knowledge base, which is used to reason through a problem, using the
knowledge that is appropriate.
An important advantage here is that within the domain of the knowledge base, a different
problem can be solved using the same program without reprogramming efforts. Moreover,
expert systems could explain the reasoning process and handle levels of confidence and
uncertainty, which conventional algorithms do not handle (Giarratano and Riley, 1989). Some
of the important advantages of expert systems are as follows:
ability to capture and preserve irreplaceable human experience;
ability to develop a system more consistent than human experts;
minimize human expertise needed at a number of locations at the same time (especially in
a hostile environment that is dangerous to human health);
solutions can be developed faster than human experts.
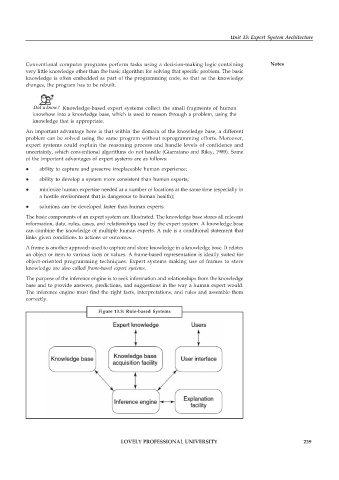
The basic components of an expert system are illustrated. The knowledge base stores all relevant
information, data, rules, cases, and relationships used by the expert system. A knowledge base
can combine the knowledge of multiple human experts. A rule is a conditional statement that
links given conditions to actions or outcomes.
A frame is another approach used to capture and store knowledge in a knowledge base. It relates
an object or item to various facts or values. A frame-based representation is ideally suited for
object-oriented programming techniques. Expert systems making use of frames to store
knowledge are also called frame-based expert systems.
The purpose of the inference engine is to seek information and relationships from the knowledge
base and to provide answers, predictions, and suggestions in the way a human expert would.
The inference engine must find the right facts, interpretations, and rules and assemble them
correctly.
Figure 13.3: Rule-based Systems
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 239