Page 130 - DCAP516_COMPUTER_SECURITY
P. 130
Computer Security
Notes
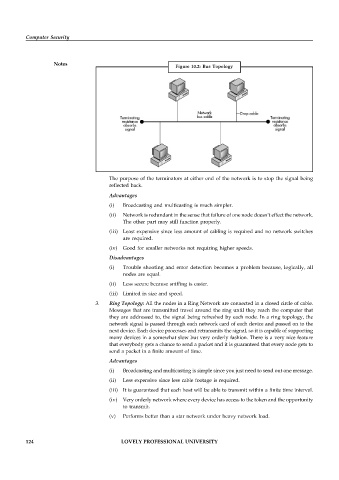
Figure 10.2: Bus Topology
The purpose of the terminators at either end of the network is to stop the signal being
reflected back.
Advantages
(i) Broadcasting and multicasting is much simpler.
(ii) Network is redundant in the sense that failure of one node doesn’t effect the network.
The other part may still function properly.
(iii) Least expensive since less amount of cabling is required and no network switches
are required.
(iv) Good for smaller networks not requiring higher speeds.
Disadvantages
(i) Trouble shooting and error detection becomes a problem because, logically, all
nodes are equal.
(ii) Less secure because sniffing is easier.
(iii) Limited in size and speed.
3. Ring Topology: All the nodes in a Ring Network are connected in a closed circle of cable.
Messages that are transmitted travel around the ring until they reach the computer that
they are addressed to, the signal being refreshed by each node. In a ring topology, the
network signal is passed through each network card of each device and passed on to the
next device. Each device processes and retransmits the signal, so it is capable of supporting
many devices in a somewhat slow but very orderly fashion. There is a very nice feature
that everybody gets a chance to send a packet and it is guaranteed that every node gets to
send a packet in a finite amount of time.
Advantages
(i) Broadcasting and multicasting is simple since you just need to send out one message.
(ii) Less expensive since less cable footage is required.
(iii) It is guaranteed that each host will be able to transmit within a finite time interval.
(iv) Very orderly network where every device has access to the token and the opportunity
to transmit.
(v) Performs better than a star network under heavy network load.
124 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY