Page 146 - DCAP103_Principle of operating system
P. 146
Unit 4: Process Management-III
otherwise, Finish[i] := true. Notes
2. Find an index i such that both
a. Finish[i] =false.
b. Requesti 5 Work.
If no such i exists, go to step 4.
3. Work := Work + Allocationi
Finish[i] := true go to step 2.
4. If Finish[i] = false, for some i, 1 _< i 5 n, then the system is in a deadlock state. Moreover,
if Finish[i] =false, then process Pi is deadlocked. This algorithm requires an order of m x n2
operations to detect whether the system is in a deadlocked state. You may wonder why we
reclaim the resources of process Pi (in step 3) as soon as we determine that Requesti _< Work
(in step 2b). We know that Pi is currently not involved in a deadlock (since Requesti < Work).
Thus, we take an optimistic attitude, and assume that Pi will require no more resources to
complete its task; it will thus soon return all currently allocated resources to the system. If our
assumption is incorrect, a deadlock may occur later. That deadlock will be detected the next
time that the deadlock-detection algorithm is invoked. To illustrate this algorithm, we consider
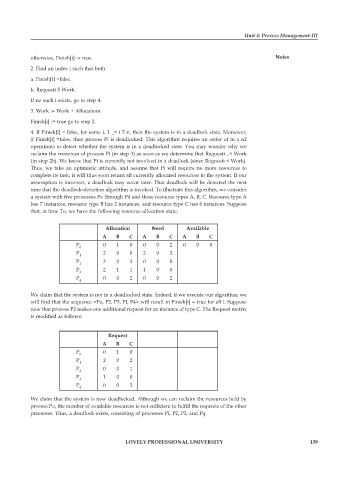
a system with five processes Po through P4 and three resource types A, B, C. Resource type A
has 7 instances, resource type B has 2 instances, and resource type C has 6 instances. Suppose
that, at time To, we have the following resource-allocation state:
Allocation Need Available
A B C A B C A B C
P 0 0 1 0 0 0 2 0 0 0
P 1 2 0 0 2 0 2
P 2 3 0 3 0 0 0
P 3 2 1 1 1 0 0
P 4 0 0 2 0 0 2
We claim that the system is not in a deadlocked state. Indeed, if we execute our algorithm, we
will find that the sequence <Po, P2, P3, PI, P4> will result in Finish[i] = true for all i. Suppose
now that process P2 makes one additional request for an instance of type C. The Request matrix
is modified as follows:
Request
A B C
P 0 0 1 0
P 1 2 0 2
P 2 0 0 1
P 3 1 0 0
P 4 0 0 2
We claim that the system is now deadlocked. Although we can reclaim the resources held by
process Po, the number of available resources is not sufficient to fulfill the requests of the other
processes. Thus, a deadlock exists, consisting of processes PI, P2, P3, and Pq.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 139