Page 256 - DCAP103_Principle of operating system
P. 256
Unit 7: Secondary Storage Structure
Notes
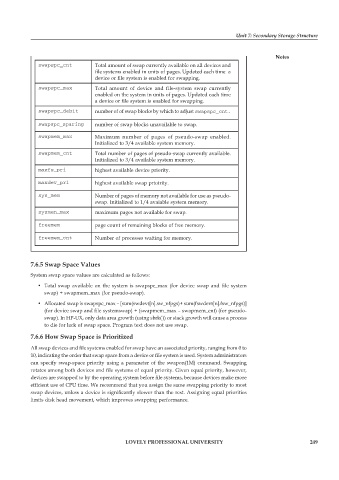
swapspc_cnt Total amount of swap currently available on all devices and
file systems enabled in units of pages. Updated each time a
device or file system is enabled for swapping.
swapspc_max Total amount of device and file-system swap currently
enabled on the system in units of pages. Updated each time
a device or file system is enabled for swapping.
swapspc_debit number of of swap blocks by which to adjust swapspc_cnt.
swapspc_sparing number of swap blocks unavailable to swap.
swapmem_max Maximum number of pages of pseudo-swap enabled.
Initialized to 3/4 available system memory.
swapmem_cnt Total number of pages of pseudo-swap currently available.
Initialized to 3/4 available system memory.
maxfs_pri highest available device priority.
maxdev_pri highest available swap prioirity.
sys_mem Number of pages of memory not available for use as pseudo-
swap. Initialized to 1/4 avaiable system memory.
sysmen_max maximum pages not available for swap.
freemem page count of remaining blocks of free memory.
freemem_cnt Number of processes waiting for memory.
7.6.5 Swap Space Values
System swap space values are calculated as follows:
• Total swap available on the system is swapspc_max (for device swap and file system
swap) + swapmem_max (for pseudo-swap).
• Allocated swap is swapspc_max – [sum(swdevt[n].sw_nfpgs)+ sum(fswdevt[n].fsw_nfpgs)]
(for device swap and file systemswap) + (swapmem_max – swapmem_cnt) (for pseudo-
swap). In HP-UX, only data area growth (using sbrk( )) or stack growth will cause a process
to die for lack of swap space. Program text does not use swap.
7.6.6 How Swap Space is Prioritized
All swap devices and file systems enabled for swap have an associated priority, ranging from 0 to
10, indicating the order that swap space from a device or file system is used. System administrators
can specify swap-space priority using a parameter of the swapon(1M) command. Swapping
rotates among both devices and file systems of equal priority. Given equal priority, however,
devices are swapped to by the operating system before file systems, because devices make more
efficient use of CPU time. We recommend that you assign the same swapping priority to most
swap devices, unless a device is significantly slower than the rest. Assigning equal priorities
limits disk head movement, which improves swapping performance.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 249