Page 386 - DCAP103_Principle of operating system
P. 386
Unit 13: Input/Output and Security of Windows
13.2.2 File System API Calls in Windows 2000 Notes
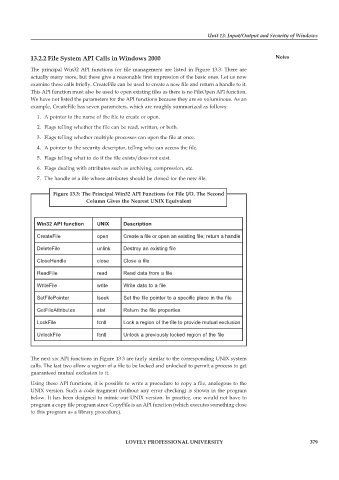
The principal Win32 API functions for file management are listed in Figure 13.3. There are
actually many more, but these give a reasonable first impression of the basic ones. Let us now
examine these calls briefly. CreateFile can be used to create a new file and return a handle to it.
This API function must also be used to open existing files as there is no FileOpen API function.
We have not listed the parameters for the API functions because they are so voluminous. As an
example, CreateFile has seven parameters, which are roughly summarized as follows:
1. A pointer to the name of the file to create or open.
2. Flags telling whether the file can be read, written, or both.
3. Flags telling whether multiple processes can open the file at once.
4. A pointer to the security descriptor, telling who can access the file.
5. Flags telling what to do if the file exists/does not exist.
6. Flags dealing with attributes such as archiving, compression, etc.
7. The handle of a file whose attributes should be cloned for the new file.
Figure 13.3: The Principal Win32 API Functions for File I/O. The Second
Column Gives the Nearest UNIX Equivalent
Win32 API function UNIX Description
CreateFile open Create a file or open an existing file; return a handle
DeleteFile unlink Destroy an existing file
CloseHandle close Close a file
ReadFile read Read data from a file
WriteFile write Write data to a file
SetFilePointer lseek Set the file pointer to a specific place in the file
GetFileAttributes stat Return the file properties
LockFile fcntl Lock a region of the file to provide mutual exclusion
UnlockFile fcntl Unlock a previously locked region of the file
The next six API functions in Figure 13.3 are fairly similar to the corresponding UNIX system
calls. The last two allow a region of a file to be locked and unlocked to permit a process to get
guaranteed mutual exclusion to it.
Using these API functions, it is possible to write a procedure to copy a file, analogous to the
UNIX version. Such a code fragment (without any error checking) is shown in the program
below. It has been designed to mimic our UNIX version. In practice, one would not have to
program a copy file program since CopyFile is an API function (which executes something close
to this program as a library procedure).
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 379