Page 77 - DCAP103_Principle of operating system
P. 77
Principles of Operating Systems
Notes
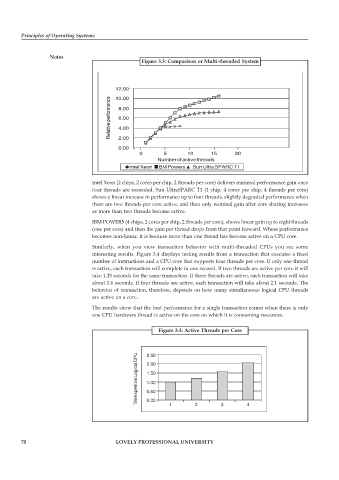
Figure 3.3: Comparison or Multi-threaded System
Intel Xeon (2 chips, 2 cores per chip, 2 threads per core) delivers minimal performance gain once
four threads are exceeded. Sun UltraSPARC T1 (1 chip, 4 cores per chip, 4 threads per core)
shows a linear increase in performance up to four threads, slightly degraded performance when
there are two threads per core active, and then only nominal gain after core sharing increases
as more than two threads become active.
IBM POWER5 (4 chips, 2 cores per chip, 2 threads per core), shows linear gain up to eight threads
(one per core) and then the gain per thread drops from that point forward. Where performance
becomes non-linear, it is because more than one thread has become active on a CPU core.
Similarly, when you view transaction behavior with multi-threaded CPUs you see some
interesting results. Figure 3.4 displays testing results from a transaction that executes a fixed
number of instructions and a CPU core that supports four threads per core. If only one thread
is active, each transaction will complete in one second. If two threads are active per core it will
take 1.25 seconds for the same transaction. If three threads are active, each transaction will take
about 1.6 seconds. If four threads are active, each transaction will take about 2.1 seconds. The
behavior of transaction, therefore, depends on how many simultaneous logical CPU threads
are active on a core.
The results show that the best performance for a single transaction comes when there is only
one CPU hardware thread is active on the core on which it is consuming resources.
Figure 3.4: Active Threads per Core
70 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY