Page 236 - DCAP104_EXPOSURE_TO_COMPUTER_DISCPLINES
P. 236
Unit 12: System Development Life Cycle
Notes
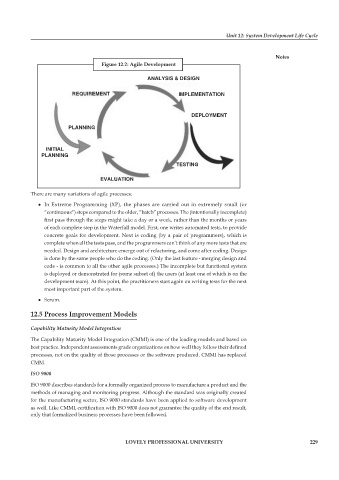
Figure 12.2: Agile Development
ANALYSIS & DESIGN
REQUIREMENT IMPLEMENTATION
DEPLOYMENT
PLANNING
INITIAL
PLANNING
TESTING
EVALUATION
There are many variations of agile processes:
In Extreme Programming (XP), the phases are carried out in extremely small (or
“continuous”) steps compared to the older, “batch” processes. The (intentionally incomplete)
first pass through the steps might take a day or a week, rather than the months or years
of each complete step in the Waterfall model. First, one writes automated tests, to provide
concrete goals for development. Next is coding (by a pair of programmers), which is
complete when all the tests pass, and the programmers can’t think of any more tests that are
needed. Design and architecture emerge out of refactoring, and come after coding. Design
is done by the same people who do the coding. (Only the last feature - merging design and
code - is common to all the other agile processes.) The incomplete but functional system
is deployed or demonstrated for (some subset of) the users (at least one of which is on the
development team). At this point, the practitioners start again on writing tests for the next
most important part of the system.
Scrum.
12.5 Process Improvement Models
Capability Maturity Model Integration
The Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI) is one of the leading models and based on
best practice. Independent assessments grade organizations on how well they follow their defined
processes, not on the quality of those processes or the software produced. CMMI has replaced
CMM.
ISO 9000
ISO 9000 describes standards for a formally organized process to manufacture a product and the
methods of managing and monitoring progress. Although the standard was originally created
for the manufacturing sector, ISO 9000 standards have been applied to software development
as well. Like CMMI, certification with ISO 9000 does not guarantee the quality of the end result,
only that formalized business processes have been followed.
LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY 229