Page 97 - DCAP104_EXPOSURE_TO_COMPUTER_DISCPLINES
P. 97
Exposure to Computer Disciplines
Notes
1. Logical topologies are often closely associated with Media Access Control
methods and protocols.
2. The logical topologies are generally determined by network protocols as
opposed to being determined by the physical layout of cables, wires, and
network devices or by the flow of the electrical signals, although in many
cases the paths that the electrical signals take between nodes may closely
match the logical flow of data, hence the convention of using the terms
logical topology and signal topology interchangeably.
3. Logical topologies are able to be dynamically reconfigured by special types
of equipment such as routers and switches.
Daisy Chains
Except for star-based networks, the easiest way to add more computers into a network
is by daisy-chaining, or connecting each computer in series to the next. If a message is
intended for a computer partway down the line, each system bounces it along in sequence until
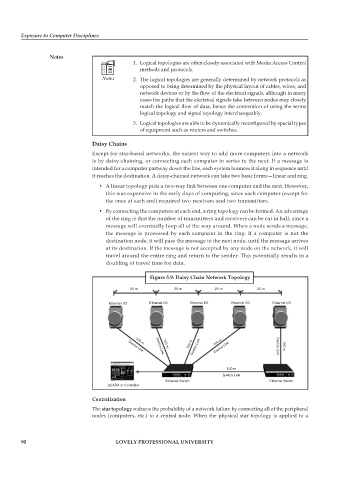
it reaches the destination. A daisy-chained network can take two basic forms—linear and ring.
• A linear topology puts a two-way link between one computer and the next. However,
this was expensive in the early days of computing, since each computer (except for
the ones at each end) required two receivers and two transmitters.
• By connecting the computers at each end, a ring topology can be formed. An advantage
of the ring is that the number of transmitters and receivers can be cut in half, since a
message will eventually loop all of the way around. When a node sends a message,
the message is processed by each computer in the ring. If a computer is not the
destination node, it will pass the message to the next node, until the message arrives
at its destination. If the message is not accepted by any node on the network, it will
travel around the entire ring and return to the sender. This potentially results in a
doubling of travel time for data.
Figure 5.9: Daisy Chain Network Topology
20 m 20 m 20 m 20 m
Ethernet I/O Ethernet I/O Ethernet I/O Ethernet I/O Ethernet I/O
100 m Device Link 100 m Device Link 100 m
Device Link
100 m
100 m
Device Link
Device Link
100 m
Switch Link
Ethernet Switch Ethernet Switch
SCADA or Controller
Centralization
The star topology reduces the probability of a network failure by connecting all of the peripheral
nodes (computers, etc.) to a central node. When the physical star topology is applied to a
90 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY