Page 77 - DCAP404 _Object Oriented Programming
P. 77
Object-oriented Programming
Notes class <class_name>
{
private:
variables declaration;
function declarations;
public:
variable declaration;
function declarations;
};
The class declaration is similar to a struct declaration. The keyword class specifies that what
follows is an abstract data of type class_name. The body of a class is enclosed within braces and
terminated by a semicolon. The class body contains the declaration of variables and functions.
These functions and variables are collectively called members. They are usually grouped under
two sections, namely, private and public to denote which of the members are private and which
of them are public. The keywords private and public are known as visibility labels.
The members that have been declared as private can be accessed only from within the class. On
the other hand, public members can be accessed from outside the class also. The data hiding
(using private declaration) is the key feature of object-oriented programming. The use of the
keyword private is optional. By default, the members of a class are private. If both the labels are
missing, then, by default, all the members are private. Such a class is completely hidden from
the outside world and does not serve any purpose.
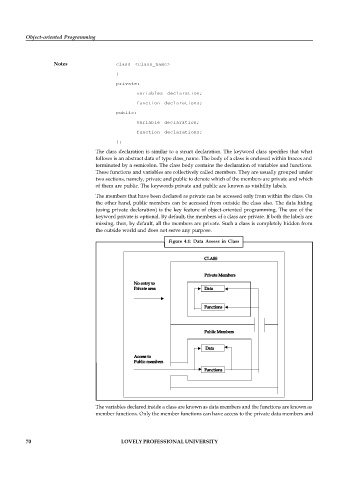
Figure 4.1: Data Assess in Class
CLASS
Private Members
No entry to
Private area Data
Functions
Public Members
Data
Access to
Public members
Functions
The variables declared inside a class are known as data members and the functions are known as
member functions. Only the member functions can have access to the private data members and
70 LOVELY PROFESSIONAL UNIVERSITY